It all started in 1998 when Marc Randolph wanted a large category of portable items to be sold over the internet using a business model similar to Amazon. Netflix launched as the world’s first online DVD-rental store, and today has become a medium, which changed the way how many people spend their time. Even though there are competitions like Amazon Prime, Disney Hotstar, etc., Netflix is by far the leader serving close to 200 million customers.
Have you ever pondered about the innovation and tech behind such a successful business that provides quality content to multiple users over approximately 190 geographic locations covered in almost 10 languages? We have conducted a patent portfolio analysis to answer some of these questions.
Netflix’s Patent Portfolio Build Up Strategy at A Glance
Netflix believes that almost 80% of its watched content is based on its algorithmic recommendations and it is the foundation of what we see today. The innovation of Netflix ranges from machine learning for content recommendation to providing an exhilarating user experience to its customers.
Netflix has been filing patent applications from its initial years of DVD renting. Prominent examples of its work include the rental processing system (US7848968B1), envelopes in usage(US7401727B2), its sharing rental account(US7958529B2), and the rental management system(US8972290B2).
Over the years, and multiple business model transitions later, Netflix’s patented technology today works to provide a streamlined user experience and a comfortable viewing experience whilst maximizing consumer engagement to ensure the viewer returns to Netflix’s services time and again.
The major research areas of Netflix Patents are shown below:
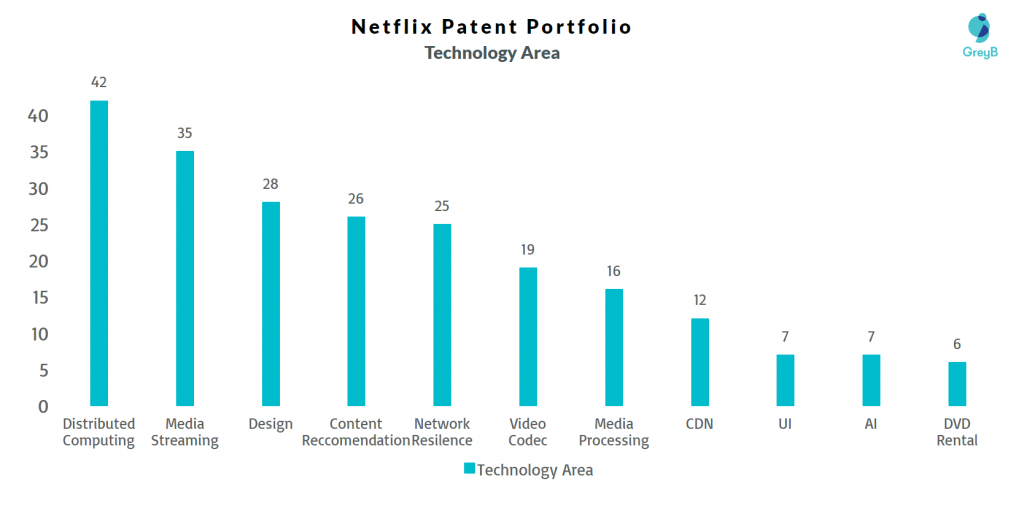
Netflix is leaving no stone unturned to ensure providing a supreme experience to its users with patent families in each domain related to content streaming.
From using AI for content recommendations to providing quality content with the minimum of buffering and downtime, Netflix has transformed itself from a physical business to a digital content powerhouse.
Let’s see what kind of patents are in each of these technology cluster one at a time:
Netflix Distributed Computing Patents (42 patent families)
Netflix is huge, it has a lot of subscribers, they play a lot of videos, but how do they keep their subscribers happy? It is the cloud computing that Netflix adopted in 2010. Actually, Netflix uses 2 different clouds: AWS and OpenConnect, both of which must work together to provide endless hours of customer-pleasing videos.
We can think of it like the moments before and after the pressing of the play button. Everything that happens before you hit play happens in the backend, which runs in AWS.
Anything that doesn’t involve serving video is handled by AWS. This includes scalable computing, scalable storage, scalable distributed databases, big data processing and analytics, recommendations, transcoding, and hundreds of other functions.
Netflix has filed multiple patents in the distributed computing domain- ranging from media processing to CDN which will discuss in the below sections.
In this patent cluster, Netflix patents on managing the backend and innovating different solutions for improved performance– for example, on the improvement of memory management (US10606510B2), task scheduling (US10671947B2), etc– are tagged.
Another patent US9430212B2 aims at automatically generating cloud-based working virtual instances. This not only saves time but also makes the new software updates to be installed with the least error.
Many of Netflix’s Distributed Computing patents deal with the different levels of cache memory for presenting the content to the end-users. These inventions aim at content storage and delivery as per the network capacity of an end-user.
Patents in the cluster also ensure the elimination of the wait time. One good example of cache storage has been illustrated in the patent US20160321286A1 where maintaining different copies of the video/audio content is done while also maintaining synchronization among the network centers.
Netflix Media Streaming Patents (35 patent families)
The patents in this cluster more precisely aim at efficient client-server communication for optimized playback and content streaming (US8365235B2).
Netflix’s binge-watching patent (US10452919B2) is also part of this cluster. Who wants to see the credits sections while a series or a TV show? The patent skips the unwanted section and lets you stay hooked to the main content.
Patents of the cluster also discuss techniques for managing video playback on multiple devices (US20170337048A1 ) along with maintaining synchronization between the audio and video (US20120042047A1).
Many patents in the cluster are related to transitions (US9762936B2) between the scenes, and instances where the transition of audio starts between the transition of the video (US8682139B2).
Content Recommendation (26 patent families):
Netflix’s recommendation system is at the core of the product. It comes with the ability to reduce the time and effort to find something great to watch. All this is done by continual processing of the gigantic amount of data about what content users watch, where they watch along, and how they interact with the service.
Obviously, every person has their own taste and preferences which makes personalized recommendation a far more challenging task. Netflix works on integrating more of a human element into its systems and letting the content speak for itself.
At Netflix, they go beyond recommending movie titles and also use recommendation engines to curate the preview images (US10573039B2) you’re seeing on your feed. If you rate Johnny Depp highly, its engine will likely show the image of Jack Sparrow while recommending Pirates of the Caribbean. The Wired has explained this intuitively in this blog.
As explained above, Netflix uses machine learning for building its recommendation systems. The present cluster contains patents that relate to the data collection, processing (US10360508B1), and training of the statistical models for recommending items based on user’s behavior.
The data is a plurality of the genres, categories, actors, release date, time of the day you are watching, a device used, geographic location, etc. All these pieces of data are used as an input for processing the algorithm that helps in achieving scalability by recommending the most appropriate content to its users.
Along with the recommendation of movie titles, Netflix’s recommendation engine also ranks (US8903834B2) the movie titles based on the user’s taste and preferences.
Network Resilience or Chaos Engineering Patents by Netflix (25 patent families)
2010 marked the year when Netflix switched to cloud computing. Switching to such a diverse domain invited a lot of problems. The host resources (such as cache and databases) could be terminated and replaced at any time, which meant their services needed to prepare for this constraint.
Netflix designed the Chaos Monkey tool for testing system stability by enforcing failures within its architecture. Basically testing how their system would perform when the critical components of their services were taken down.
This was a very novel approach to identifying (US20180089011A1) and fixing failures (US9858133B2) before it became a public outage. The network resiliency was further leveraged when Netflix announced the evolution of their chaos monkey by building the Simian army.
The patents herein basically relate to chaos engineering, which has become a new engineering practice after the success of Netflix’s chaos monkey and protecting the networked environment of malicious attacks. This includes network security (US10262145B2) and data security (US10511623B2).
Although an attack need not necessarily be malicious in intent, but may rather be any undesirable behavior, including, for example, a user unintentionally over-using system resources. The patent US9954822B2 for example relates to a traffic management system and protecting the networked environment from such unintended attacks.
Netlfix Video Codec Patents (19 patent families)
Have you ever wondered how are you able to view Netflix’s content at any location- be it home, train, hotel, etc? This is all due to the behind-the-scene efforts of Netflix’s engineers who are striving to provide you quality content.
The data compression team works towards the generation of efficient video and audio codecs to refine the streaming algorithm and optimize content placement over the distributed server.
The video along with the audio that we see/hear on our devices is actually a stream of 0s and 1s that are encoded and decoded for providing a seamless experience. This stream is further divided into frames of desirable length for letting coding-decoding (codec) algorithms allow digital video and audio data to be transmitted in real-time. But due to variable network conditions, the device streaming the content may provide problems.
The patent US20200084459A1 allows for an on-device multiplexing of the audio/video data ( eg. .mp4+1080p, .avi+720p) and also adaptive bitrate switching. This allows for dynamically switching between different streams of varying quality during playback providing the users with the best experience that their bandwidth and CPU can hold.
Netflix’s video codecs patents aim towards the efficient compression techniques for different instances(US20190379895A1) and also towards the optimization of the resolution(US10404986B2) through its specialized algorithms and achieving large scale streaming.
The patents US20190281324A1 and US10674180B2 in the cluster discuss methods for optimal error management associated with the compression methods.
Netflix Media Processing Patents (16 patent families)
Media processing is also one of the most important areas of research for Netflix’s engineers. They not only work on recommendation but also on the procession of videos to ensure a smooth and reliable experience.
Ever since its switch to cloud computing, the company has devised extensive methods to deliver content that leads to a better user experience.
Conventionally, video codecs encode frames with equal time intervals which can kill the viewing experience. How will you feel while watching an action sequence where there is a lag between the fight? Rather than using time-based division for rendering content, what Netflix does is a scene-based slotting (US10140520B2) to ensure that the most appropriate scenes are delivered in continuity rather than in bits and pieces.
The media processing patents filed by Netflix deals with the production of the content that basically makes everything possible from analyzing different use cases for display (US10366476B2) to adjusting the quality of the streaming based on the network capacity (US20180220174A1).
The patent US20170249719A1 deals with the automatic adjusting of the aspect ratio to offer the best viewing experience on any screen. Another media processing patent US10586110B2 deals with automatically assessing the video content using various metrics to enhance the overall viewing experience.
Patents covering methods/techniques for the subtitle generation (US10419828B2) that also adjusts based on the scene change are also the part of Media Processing cluster.
Netflix CDN Patents (12 patent families)
Well, we started with the processing of information before pressing the play button. So far, we know how the Netflix engine recommends content to its users and how it finally streams content on our devices.
With Netflix having millions of users around the globe and not having servers all around, it has revolutionized content delivery to enhance the experience of the users through its Open Connect CDN (Content Delivery Network) platform.
The open connect basically aims at serving 100% of Netflix’s video traffic and communicating with the local ISPs for delivering the content.
The Internet is the most important technology for communicating information across the globe today. As such, it is crucial to make sure the infrastructure behind it can scale to support any current and future needs.
With the help of CDNs, this is being achieved in the most efficient manner by moving the content closer to end-users and delivering from multiple servers located at the edge of the Internet.
The patents in this cluster have their foundation in distributed computing but more specifically deals with the content delivery from the servers to the end device through the intermediate CDNs.
The patents filed for improving the performance of the CDN revolve around the management of the ISP cache (US10536498B2), and also in the management of graphic memory using glyph caching technique (US20190243770A1).
Patent US9998354B2 deals with the estimating of the closeness of the content server and your device. All these patents help in minimizing the delays in the loading of the application and increasing the uptime of the delivery of the content.
Without a CDN all the end-user requests must be responded to by the content origin servers, which may also increase the round trip time and hence unpleasant experience. Netflix has also filed patents for communication protocols for organizing the servicing of the application requests.
Netflix AI Patents (7 patent families)
“When it comes to ML use cases, our personalized video recommendations at Netflix.com are well known but even more magic takes place behind the scenes. ”
~ Ville Tuulos, machine learning infrastructure architect at Netflix:
Netflix’s AI patents are on training neural networks for media processing and for recommendation systems.
For example, patent US20200143448A1 discloses a method of recommending items to the user based on their preferences. The recommender system used in this innovation uses collaborative filtering methods for fast and precise recommendations. For your information, collaborative filtering is a method of using data and algorithms to filter a catalog predicting relevant items to the users.
The patents of the AI cluster also disclose the method of optimizing the way the machine presents the content to the viewer (US20200160889A1) along with the enhancement of the quality of streaming (US10475172B2).
The patents basically aim at solving the problems related to providing a perpetual quality of content without the need to worry about buffering and data loss.
