Imagine a future where robots seamlessly integrate into our daily lives. Sanctuary AI, a pioneering company at the forefront of artificial intelligence, has unveiled the Phoenix robot, combines autonomous decision-making, advanced sensors, and human-like dexterity to navigate complex environments, revolutionizing how machines perform precise tasks in real-world settings.
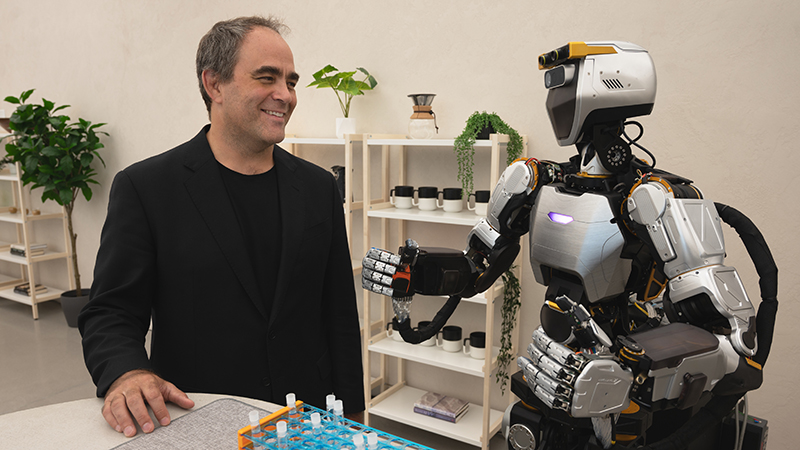

Sanctuary AI’s Phoenix robot has recently gained significant attention for its advancements in humanoid robotics, particularly following its showcase at CES 2024. Designed to autonomously handle tasks in complex environments like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing, Phoenix uses advanced sensor fusion to process visual, tactile, and environmental data in real-time. Its human-like dexterity, thanks to multi-jointed limbs, allows it to perform intricate tasks with impressive precision. With its ability to adapt to real-world conditions, Phoenix is a game-changer in robotics, offering new possibilities for industries that rely on automation and precision.
Innovations in AI and Robotics: Phoenix’s Technical Advancements
Sanctuary AI’s Phoenix robot is underpinned by several key innovations in artificial intelligence and robotics, many of which are protected through patents. These technological advancements enable Phoenix to perform tasks autonomously in complex human environments, where adaptability, precision, and decision-making are critical.
1. Autonomous Decision-Making Systems
Phoenix’s decision-making algorithms allow the autonomous processing of sensory data to prioritize tasks and adjust to real-world conditions. These systems manage obstacles and make real-time adjustments based on environmental changes.
2. Robust Control Systems for Dexterity
Phoenix’s control systems enable human-like dexterity, with multi-jointed limbs and precise hand-eye coordination. These systems allow Phoenix to manipulate objects in delicate environments, such as healthcare or manufacturing.
3. Sensor Fusion for Enhanced Perception
Phoenix integrates multiple sensors (visual, tactile, environmental) through sensor fusion techniques. This allows Phoenix to perceive and react to its environment with accuracy, avoiding collisions and adapting to real-time changes.
4. Mobility and Adaptation in Dynamic Environments
Phoenix’s mobility systems ensure smooth navigation in unpredictable environments. Algorithms for balance control, path planning, and obstacle avoidance allow Phoenix to operate in challenging spaces with ease.
Patents related to Phoenix Humanoid Robot:
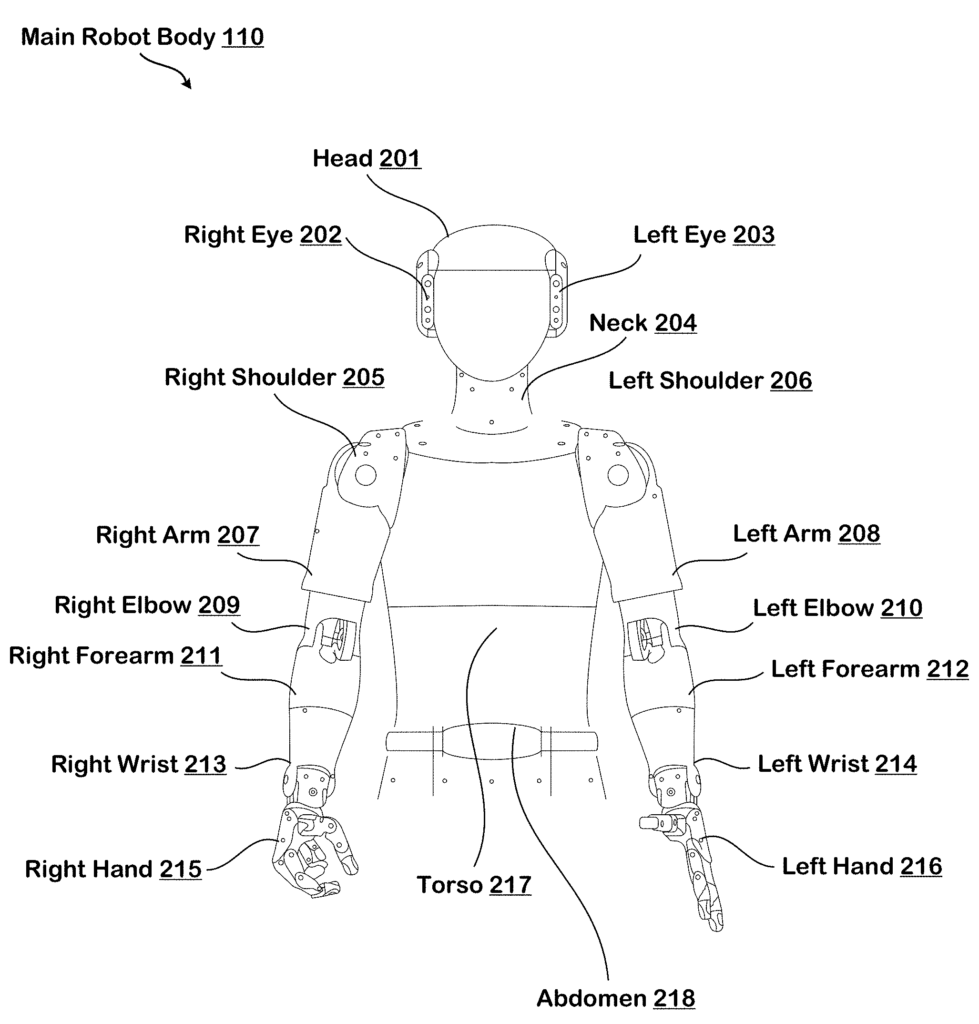
1. AI-controlled robot with Tendon-Based Joints
This patent describes US11787050B1 that this robot has a system of joints and links, starting from a base and ending with a tool or hand. It uses tendons connected to motors at the base to move the joints. These tendons may lose some precision due to their variability. To fix this, the robot’s controller uses sensors and images to adjust motor commands, ensuring precise movements despite any tendon limitations.
2. Systems and Methods for Enhancing Robot Autonomy
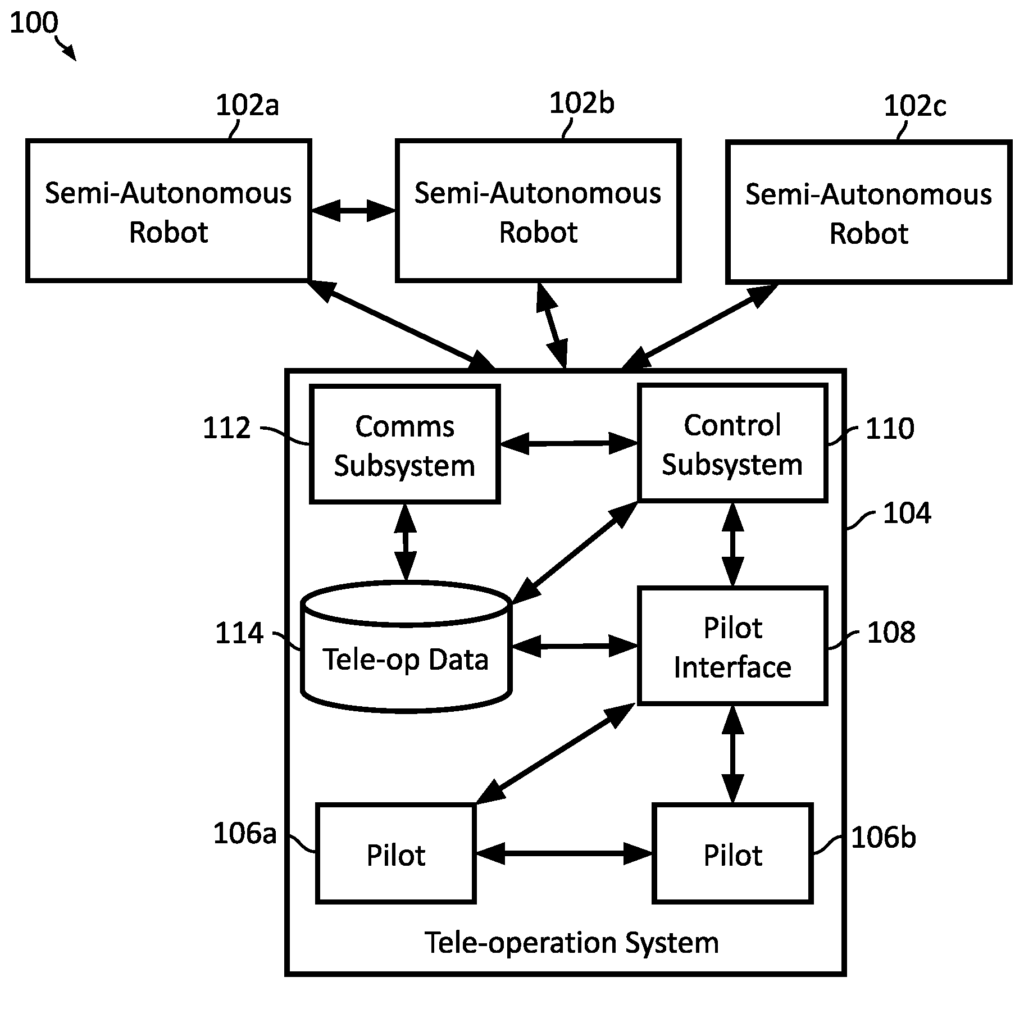
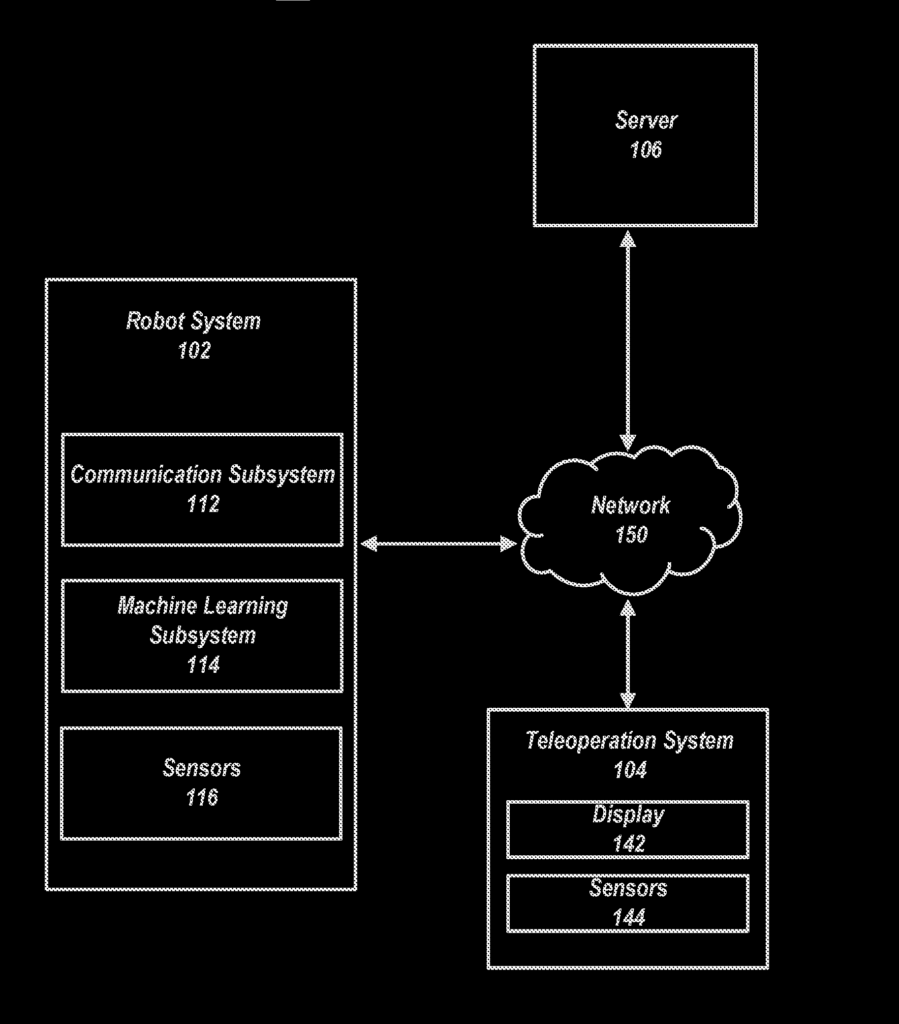
This patent US20220324113A1 describes the method allows a robot to identify possible actions it can take and gather related information for each action. When the robot is unsure about which action to choose, it sends a request for help to a remote control system, including the possible actions and related data. The robot then receives and follows the instructions from the remote system. After executing the instructions, the robot updates its control model to improve its ability to make decisions on its own in the future.
3. Teleoperation for Training Robots with Machine Learning
This patent US20230148120A1 describes a method that uses a teleoperation system to train robots via machine learning. A human operator controls the robot, and their actions are recorded. The teleoperation system provides feedback, such as vibrations, video, or sound, allowing the operator to sense the robot’s environment. Visual guides also help the operator control the robot to complete tasks more effectively. This process helps the robot learn to perform tasks through the human’s input and feedback.
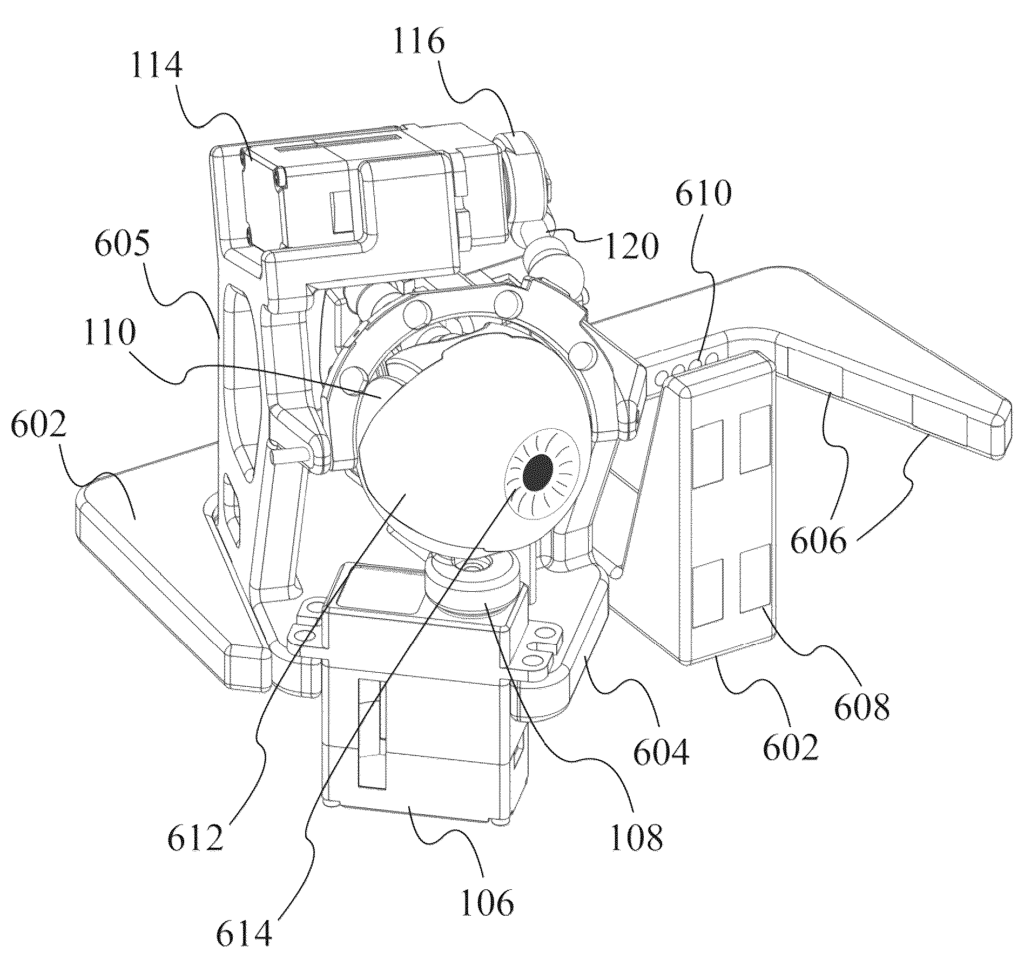
4. Detachable Mechanical Eye Cartridge for Robots
This patent US11812126B2 describes a detachable mechanical eye cartridge that includes multiple parts like links, couplers, and electronic connections, allowing the eye to move in two directions. It may have actuators for eye movement and eyelid control, along with sensors inside the eye. The cartridge can have one or two eyes and uses magnetic couplers to attach to a robot’s head. It also has mechanisms to precisely control the eye’s pitch with minimal movement errors.
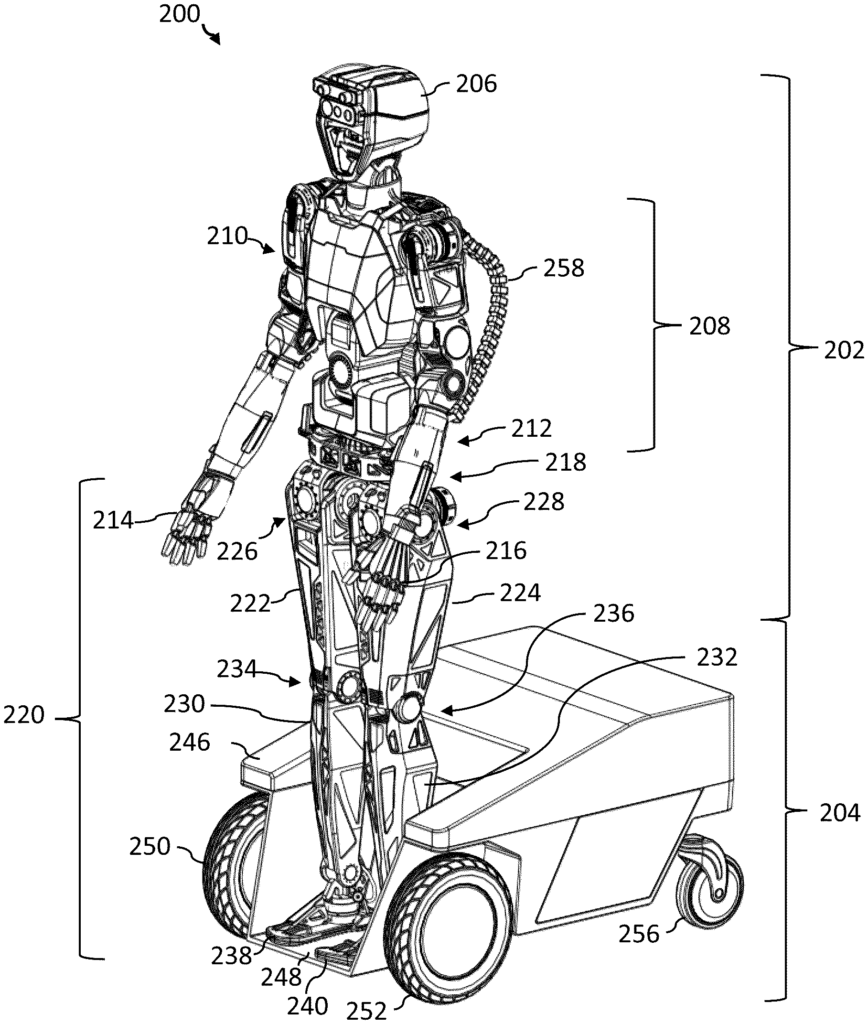
5. Humanoid Robot with Mobile Base
This patent US20240109612A1 describes a robot that has a body with two robotic legs and a torso. Each leg includes a foot, a lower leg section, and an upper leg section. The feet are attached to a mobile platform that serves as the robot’s base, allowing it to move and maintain stability.
How Does Phoenix Humanoid Robots Stand Out Among Competitors?
- Boston Dynamics (Atlas): Atlas excels in navigating tough terrains and performing complex movements with advanced mobility and balance.
- SoftBank Robotics (Pepper): Pepper specializes in social interaction and customer service, using conversational skills and emotional recognition.
- Tesla (Optimus): Tesla Bot is built for tasks like lifting, carrying, and assisting in human environments, leveraging AI from Tesla’s vehicle systems.