From government-backed digital currencies in Asia to new rules for taxing crypto payments, stablecoins are quickly moving from a niche technology to a mainstream part of the global financial system.
Unlike Bitcoin or Ether, stablecoins are designed to maintain a steady value, usually by being pegged to fiat currencies like the US dollar or backed by reserves such as cash, government bonds, or other real-world assets. This stability makes them practical for everyday use.
Companies and financial institutions are increasingly adopting stablecoins for payments, settlements, and treasury operations. They offer faster transactions, lower costs, and round-the-clock availability compared to traditional banking systems. Businesses can send money across borders in minutes instead of days, without relying on multiple intermediaries. Stablecoins are also gaining traction in payroll, remittances, e-commerce, and decentralized finance (DeFi), where they serve as a reliable medium of exchange.
Governments and regulators are now paying closer attention as stablecoins move into mainstream finance. Some countries are exploring sovereign-backed stablecoins, while lawmakers are updating tax and compliance frameworks to accommodate stablecoin payments. As stablecoins shift from experimental tools to financial infrastructure, innovation around their issuance, management, and security is accelerating—reflected clearly in the growing number of stablecoin-related patents worldwide.
As stablecoins move closer to core financial infrastructure, companies are racing to protect their innovations. This shift has led to a surge in stablecoin-related patents, covering how stablecoins are issued, stabilized, transferred, regulated, and integrated into real-world payment systems.
Problems in Stablecoins and their patent driven solutions
Price Stability
Maintaining a fixed value during market volatility
Reserve-backed models, algorithmic stabilization mechanisms, oracle-based price monitoring, and automated rebalancing systems to prevent de-pegging
Security & Fraud Risks
Risks of hacking, double spending, and unauthorized minting
Multi-ledger locking mechanisms, fraud detection engines, cryptographic transaction validation, and secure custody frameworks
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating AML, KYC, tax, and cross-border regulations
Compliance-by-design architectures, embedded identity verification, jurisdiction-aware smart contracts, and programmable compliance rules
Scalability & Infrastructure
Clean-label, allergen, and formulation standards
Global regulations around additives, allergens, and dairy alternatives create complexity for manufacturers, especially when launching products across multiple markets.
Governance & Control
Managing issuance, redemption, and policy updates
Smart contract-based governance models, automated supply control systems, and issuer-controlled lifecycle management tools
Reserve Transparency
Lack of visibility into assets backing the stablecoin
On-chain proof-of-reserve systems, cryptographic attestations, automated audits, and real-time reserve disclosure frameworks
How have patent filings in stablecoin evolved over the years?
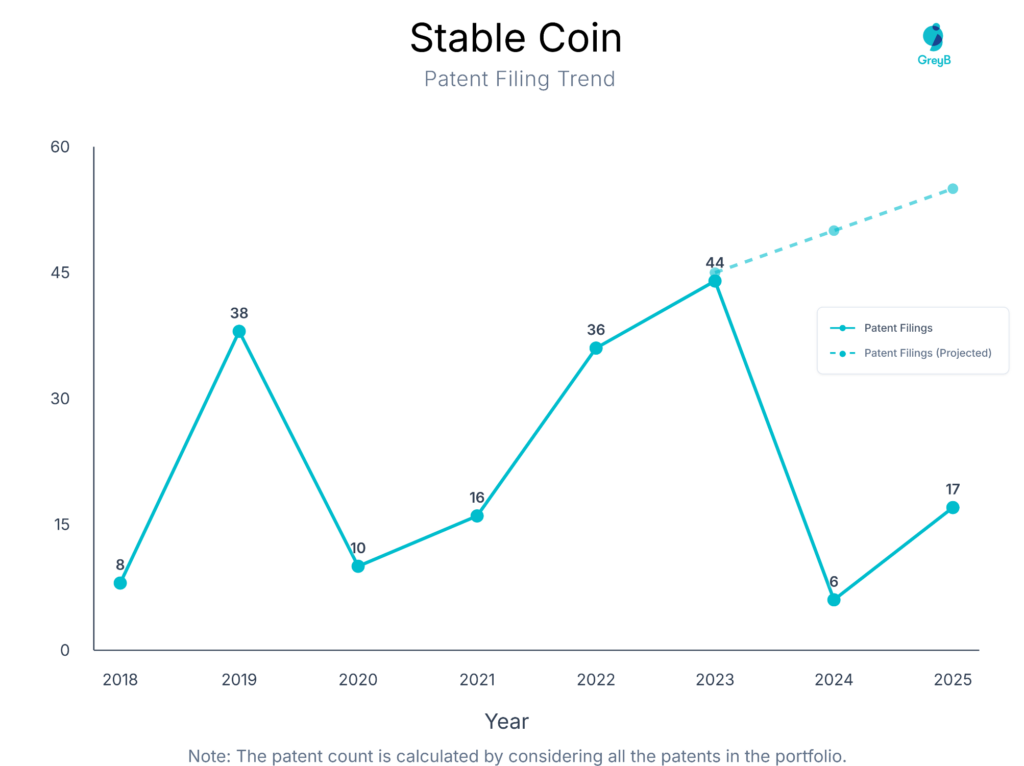
Are you wondering why there is a drop in patent filing for the last two years? It is because a patent application can take up to 18 months to get published. Certainly, it doesn’t suggest a decrease in the patent filing.
| Year of Patents Filing or Grant | Stablecoin Applications Filed | Stablecoin Patents Granted |
| 2025 | 17 | 6 |
| 2024 | 6 | 10 |
| 2023 | 44 | 8 |
| 2022 | 36 | 4 |
| 2021 | 16 | 3 |
| 2020 | 10 | 4 |
| 2019 | 38 | 3 |
| 2018 | 8 | – |
Key takeaways
Stablecoin patent activity shows clear cycles of experimentation, regulation-driven slowdown, and renewed innovation. After early experimentation in 2018, filings surged in 2019 as enterprises explored reserve-backed and payment-focused stablecoins. A temporary decline during 2020–2021 reflects market uncertainty and regulatory scrutiny.
Innovation rebounded strongly in 2022–2023, coinciding with the rise of cross-border payments, DeFi integration, compliance frameworks, and asset-backed stablecoins. The early momentum in 2025 suggests continued interest, particularly in enterprise-grade, regulated, and infrastructure-level stablecoin solutions.
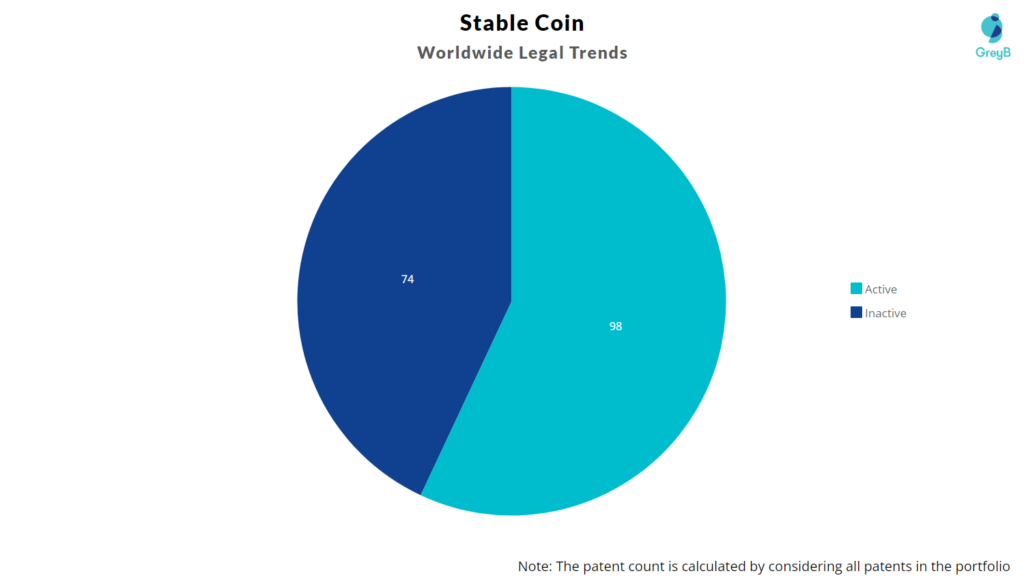
How many Stablecoin patents are Alive/Dead?
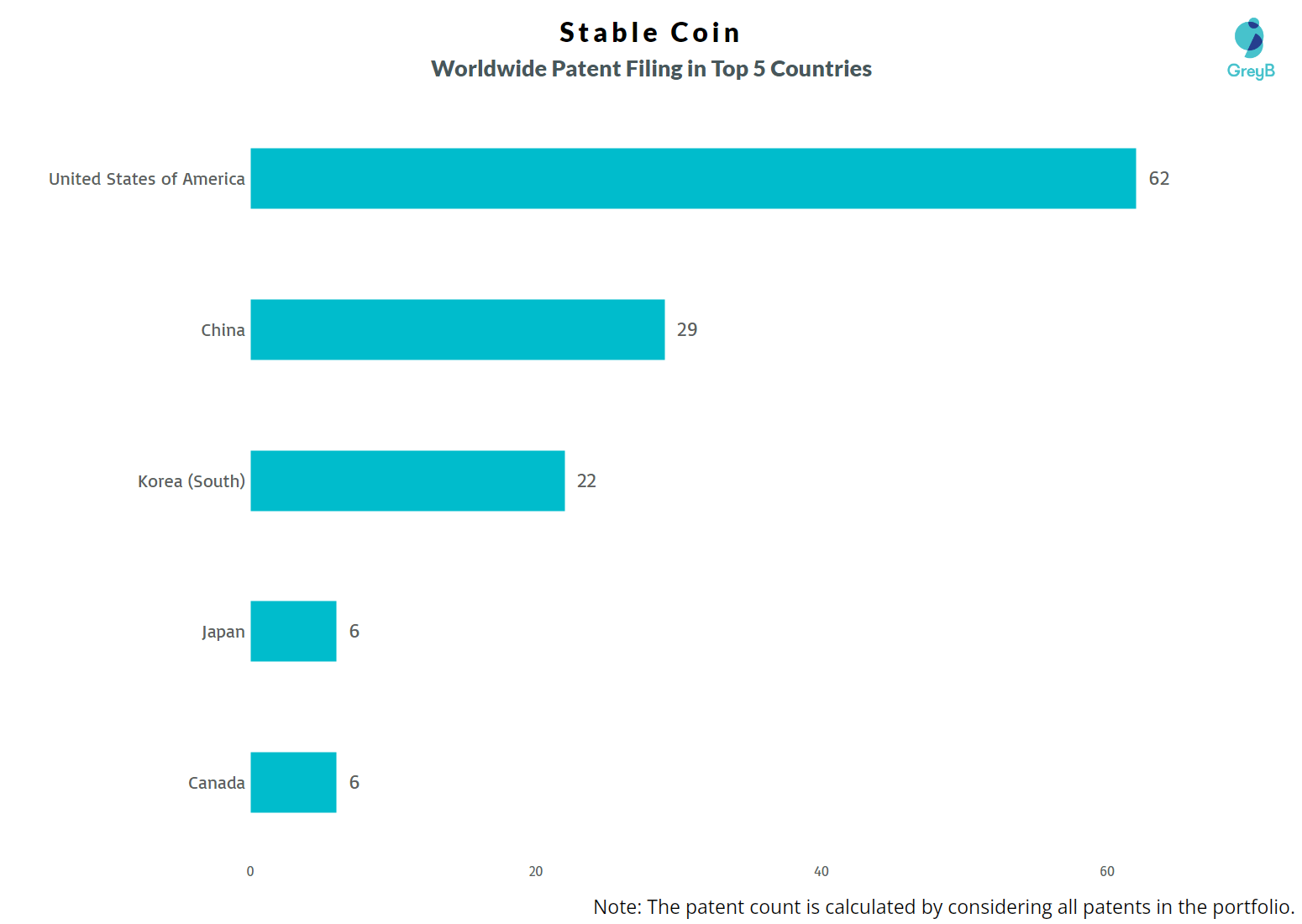
How Many Patents Stablecoin Files in Different Countries?
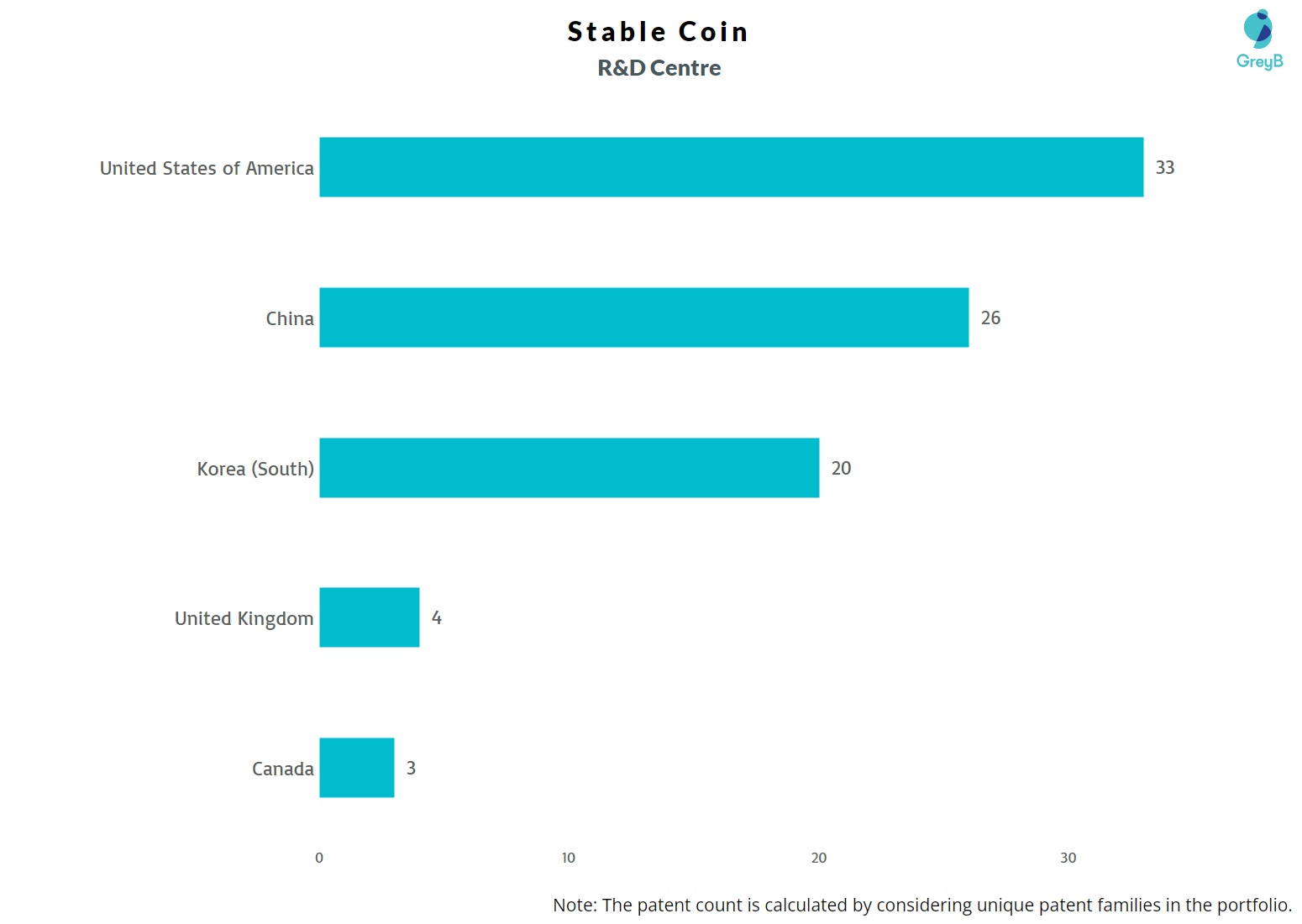
Where are Research Centers of Stablecoin Patents Located?
Who Is Leading Stablecoin Innovation Through Patent Filings?

Need the full list of the companies filing patents in stablecoin, then write to us
What Technology Areas Shape Stablecoin Patent Innovation?
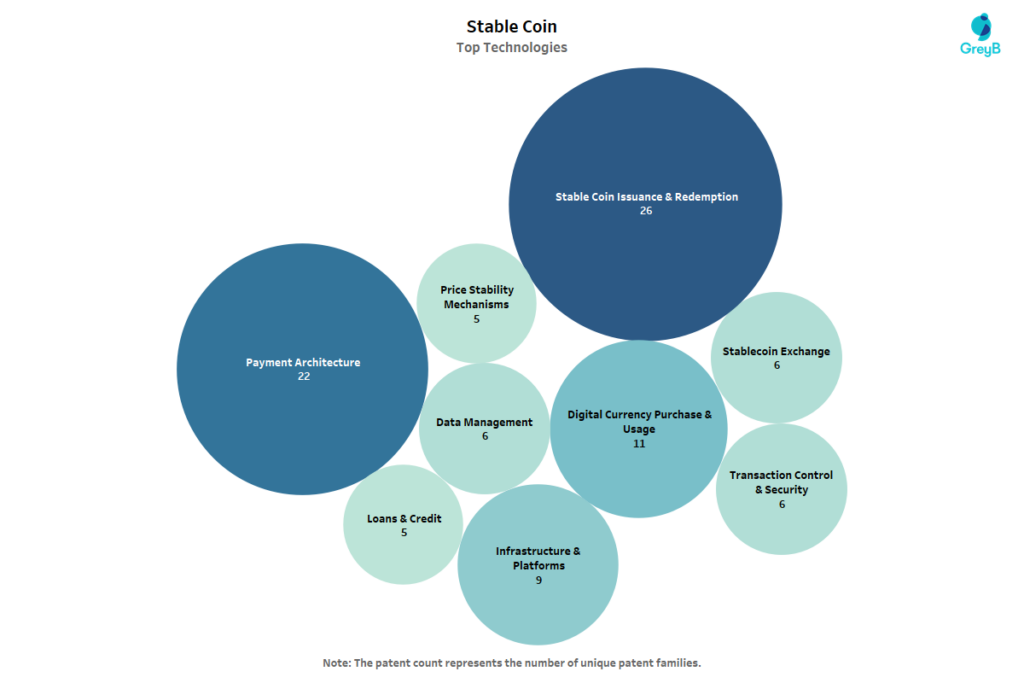
The patent landscape shows that stablecoin innovation is heavily concentrated around core infrastructure, with issuance and redemption (26 patents) and payment architecture (22 patents) forming the backbone of activity.
This indicates that companies are prioritizing scalability, reliability, and real-world usability over experimental features. Digital currency purchase and usage (11 patents) further reflects growing commercial adoption, while infrastructure and platforms (9 patents) highlight efforts to build interoperable and enterprise-ready systems.
In contrast, price stability mechanisms (5 patents) and loans and credit (5 patents) suggest these functions are increasingly embedded within broader systems rather than developed independently. Overall, the data points to a clear transition of stablecoins from experimental financial tools to mature, payment-centric digital financial infrastructure.
How Do Countries Differ Across Stablecoin Technology Areas?

The country-wise technology distribution highlights clear leaders and emerging specialization patterns in stablecoin patenting. The United States and China dominate core technology areas, particularly in stablecoin issuance and redemption (7 patents each) and payment architecture, underscoring their focus on building foundational financial infrastructure. China shows a strong tilt toward digital currency purchase and usage (6 patents), reflecting an emphasis on real-world transaction enablement.
South Korea demonstrates a well-balanced innovation profile, contributing across issuance, payments, exchanges, infrastructure, and lending, indicating holistic ecosystem development. Japan stands out in stablecoin exchange technologies with the highest activity in that category (3 patents), suggesting a focus on trading and liquidity mechanisms.
Infrastructure and platform-related patents are led by the US (4), reinforcing its strength in scalable blockchain frameworks. In contrast, price stability mechanisms remain relatively underdeveloped and geographically concentrated, mainly in the US and South Korea, signaling that algorithmic and stability-focused innovations are still in an early stage.
Get our comprehensive Stablcoin patent landscape analysis to identify “white space” opportunities, track global rivals, and mitigate infringement risks

