Groq Inc. was founded in 2016 by Jonathan Ross and is doing business in designing radically simple elegant processor architecture technology to accelerate complex workloads in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and high-performance computing. As of October 2021, Groq has a market valuation of more than $1 Billion.
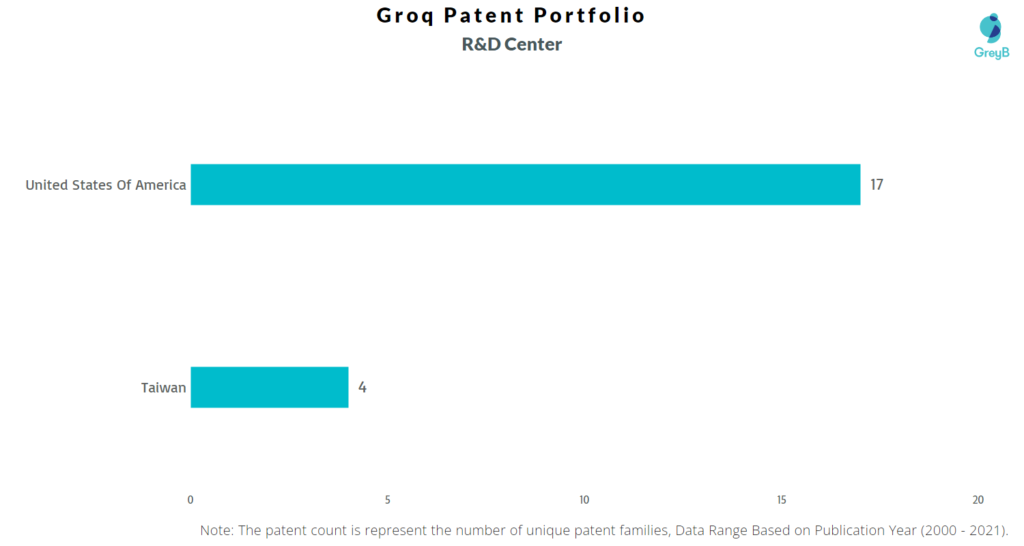
Groq has a total of 63 patents globally, out of which 21 have been granted. Of these 63 patents more than 98% patents are active. USA is where Groq has filed maximum number of patents followed by Taiwan and Europe and it also seems reasonable as the biggest market for Groq is USA, it has generated annual revenue of $41.8 million in the year 2020. Parallelly, USA seems to be the main focused R&D center and is also the origin country of Groq.
Do read about some of the most popular patents of Groq which have been covered by us in this article and also you can find Groq’s patents information, the worldwide patent filing activity and its patent filing trend over the years, and many other stats over Groq’s patent portfolio.
How many patents does Groq have?
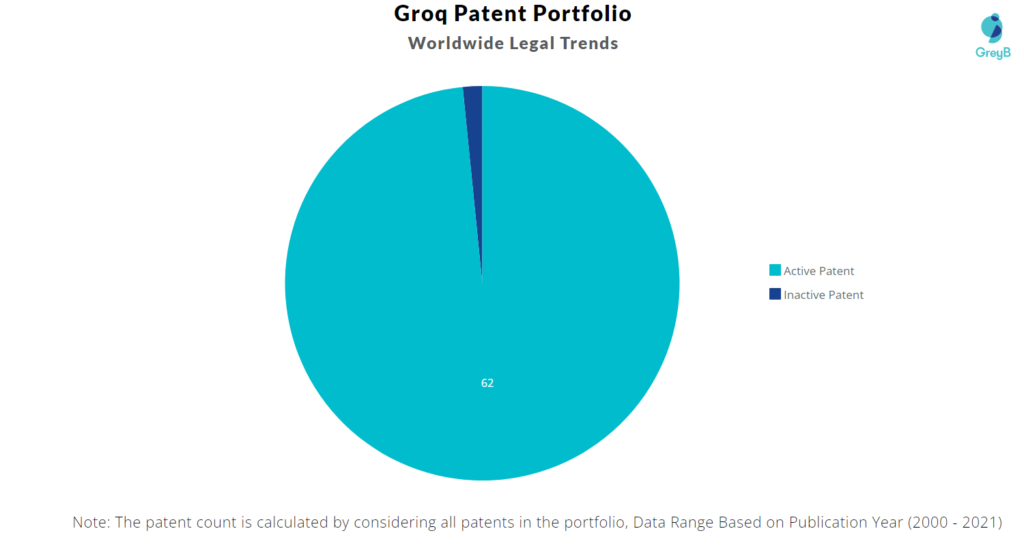
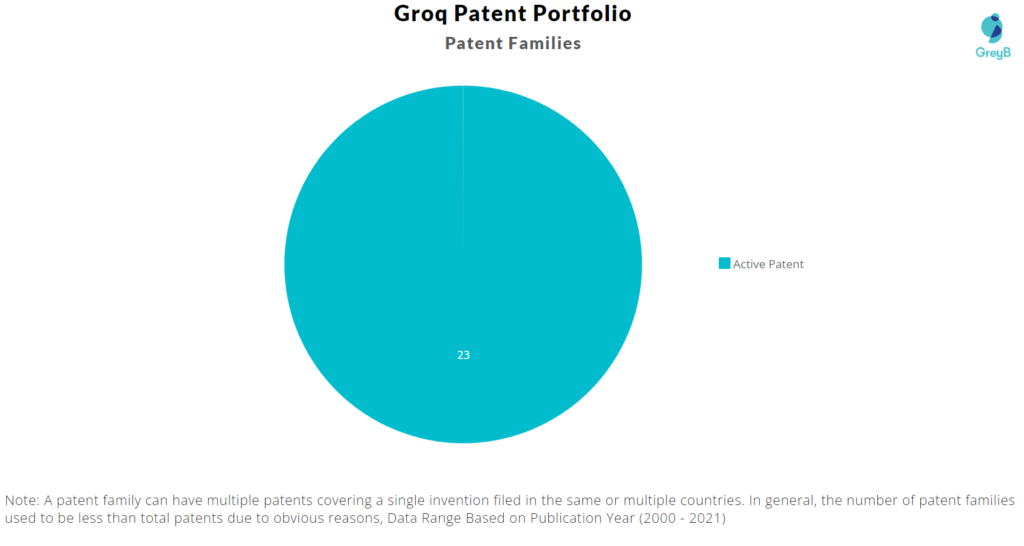
Groq has a total of 63 patents globally. These patents belong to 23 unique patent families. Out of 63 patents, 62 patents are active.
How many Groq patents are Alive/Dead?
Worldwide Patents
Patent Families
How Many Patents did Groq File Every Year?
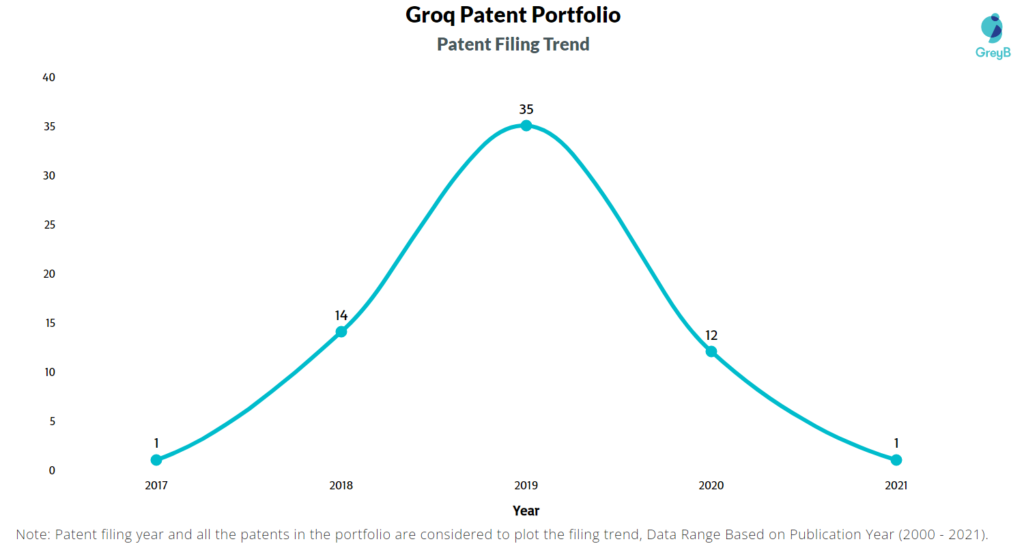
Are you wondering why there is a drop in patent filing for the last two years? It is because a patent application can take up to 18 months to get published. Certainly, it doesn’t suggest a decrease in the patent filing.
| Years of Patent Filing or Grant | Groq Application Filed | Groq Patents Granted |
| 2021 | 1 | 23 |
| 2020 | 12 | 33 |
| 2019 | 35 | 5 |
| 2018 | 14 | 2 |
| 2017 | 1 | – |
How Many Patents did Groq File in Different Countries?
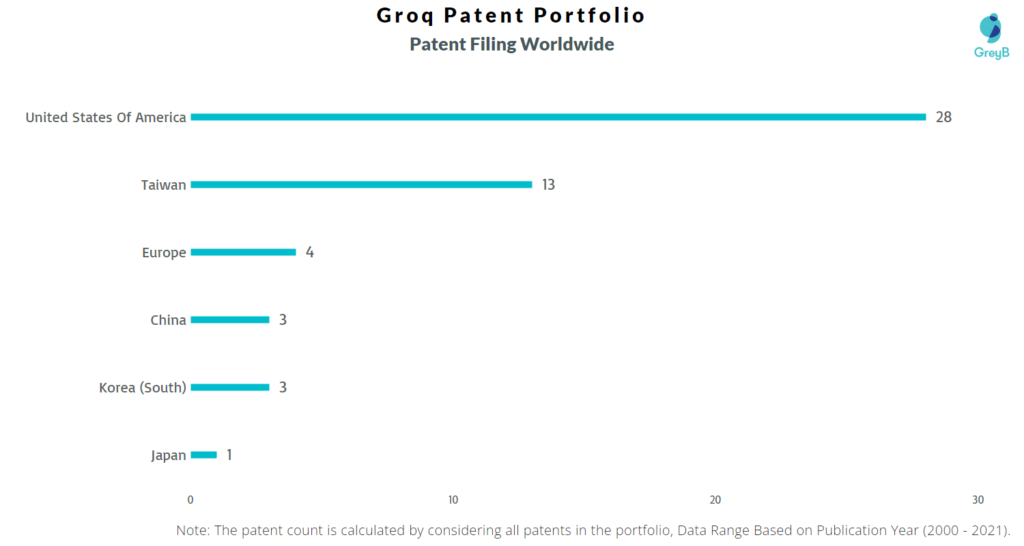
Countries in which Groq Filed Patents
| Country | Patents |
| United States Of America | 28 |
| Taiwan | 13 |
| Europe | 4 |
| China | 3 |
| Korea (South) | 3 |
| Japan | 1 |
Where are Research Centers of Groq Patents Located?
10 Best Groq Patents
US20180232663A1 is the most popular patent in the Groq portfolio. It has received 10 citations so far from companies like Amazon Technologies, Adobe Inc. and Nvidia Corporation.
| Publication Number | Citation Count |
| US20180232663A1 | 10 |
| US20200160226A1 | 4 |
| US10516383B1 | 2 |
| US10908900B1 | 1 |
| TW202034191A | 1 |
| US20190332467A1 | 1 |
| WO2018132444A1 | 1 |
| US11115147B2 | 0 |
| US11114138B2 | 0 |
| US11042360B1 | 0 |
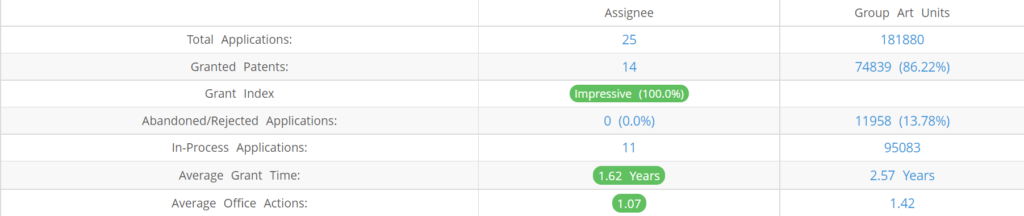
What Percentage of Groq US Patent Applications were Granted?
Groq (Excluding its subsidiaries) has filed 25 patent applications at USPTO so far (Excluding Design and PCT applications). Out of these 14 have been granted leading to a grant rate of 100%.
Which Law Firms Filed Most US Patents for Groq?
| Law Firm | Total Application | Success Rate |
| Groq Fenwick | 19 | 100.00% |
| Fenwick & West Llp | 6 | 100.00% |
“Compute’s next breakthrough will be powered by a new, simplified architectural approach to hardware and software.”
Building the computer that will power the next generation of high-performance machine learning applications. Groq hardware is engineered to be high-performing and responsive. At batch size 1, Groq’s new streamlined architecture delivers remarkable performance. Groq hardware responds faster, whether you have one image or a million.
Groq’s technology delivers lightning-fast computation while using half the energy of the nearest competition, lowering total cost of ownership and lowering carbon impact. Groq hardware has the fastest ResNet-50 performance of any commercially available hardware.
List of Groq Patents
| Publication Number | Title (English) |
| US11115147B2 | Multichip fault management |
| US11114138B2 | Data structures with multiple read ports |
| US11042360B1 | Multiplier circuitry for multiplying operands of multiple data types |
| TWI729939B | Method and processor for decompression of model parameters using functions based upon cumulative count distributions |
| US10965957B1 | Multi-pass compression of uncompressed data |
| US10938412B2 | Decompression of model parameters using functions based upon cumulative count distributions |
| TWI719433B | Data structures with multiple read ports, processor, and method for data structures with multiple read ports |
| US10908900B1 | Efficient mapping of input data to vectors for a predictive model |
| US10884485B2 | Power optimization in an artificial intelligence processor |
| US10853037B1 | Digital circuit with compressed carry |
| TWI709910B | Processors and methods of processing data |
| US10831445B1 | Multimodal digital multiplication circuits and methods |
| US10824188B2 | Multichip timing synchronization circuits and methods |
| TWI708196B | Method and processor for decompression of model parameters using functions based upon cumulative count distributions |
| US10778196B2 | Reducing power consumption in a processor circuit |
| US10776078B1 | Multimodal multiplier systems and methods |
| US10754621B2 | Tiled switch matrix data permutation circuit |
| US10725741B2 | Digital circuit with compressed carry |
| US10680644B2 | Decompression of model parameters using functions based upon cumulative count distributions |
| US10516383B1 | Reducing power consumption in a processor circuit |
| US10448054B2 | Multi-pass compression of uncompressed data |
| CN113302595A | Multi-chip timing synchronous circuit and method |
| TW202129518A | Loading operands and outputting results from a multi-dimensional array using only a single side |
| EP3844884A1 | Tiled switch matrix data permutation circuit |
| EP3841670A1 | Reducing power consumption in a processor circuit |
| EP3841461A1 | Digital circuit with compressed carry |
| CN113039541A | Space partial transformation of matrix |
| US20210195244A1 | Multi-pass compression of uncompressed data |
| KR2021066863A | Spatial Place Transformation of Matrices |
| WO2021108559A1 | Loading operands and outputting results from a multi-dimensional array using only a single side |
| US20210157767A1 | Loading operands and outputting results from a multi-dimensional array using only a single side |
| TW202117538A | Data structures with multiple read ports, processor, and method for data structures with multiple read ports |
| KR2021037726A | Reduced power consumption in the processor circuit |
| US20210081019A1 | Power optimization in an artificial intelligence processor |
| US20210004043A1 | Multichip Timing Synchronization Circuits and Methods |
| TW202046103A | Multichip timing synchronization circuits and methods |
| US20200348911A1 | Tiled switch matrix data permutation circuit |
| WO2020185239A1 | Data structures with multiple read ports |
| WO2020185238A1 | Decompression of model parameters using functions based upon cumulative count distributions |
| TW202034191A | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| TW202034190A | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| TW202034189A | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| TW202034188A | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| EP3568749A4 | Error correction in computation |
| WO2020150068A1 | Multichip timing synchronization circuits and methods |
| WO2020146153A1 | Multichip fault management |
| WO2020123541A1 | Power optimization in an artificial intelligence processor |
| TW202020654A | Digital circuit with compressed carry |
| WO2020106781A1 | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| US20200160226A1 | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| US20200159815A1 | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| US20200159814A1 | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| US20200159813A1 | Spatial locality transform of matrices |
| TW202018501A | Tiled switch matrix data permutation circuit |
| JP2020512712A | |
| WO2020060885A1 | Digital circuit with compressed carry |
| WO2020047093A1 | Tiled switch matrix data permutation circuit |
| WO2020041362A1 | Reducing power consumption in a processor circuit |
| US20190332467A1 | Error Correction in Computation |
| CN110291501A | In the calculation of error correction |
| KR2019104192A | Error correction method in operation |
| US20180232663A1 | Minimizing memory and processor consumption in creating machine learning models |
| WO2018132444A1 | Error correction in computation |


