Over the past five years, Extended Reality (XR) has matured in the background powering everything from surgical simulations at Johns Hopkins to worker training at UPS. What was once considered a novelty is now being embedded into critical workflows.
The signals are hard to ignore.
At the European Patent Office, XR-related publications rose 43% between 2016 and 2020, growing faster than the overall tech patenting rate. Leading this surge are not just hardware giants like Canon and Panasonic, but a broad mix of enterprises betting on spatial computing, sensor interfaces and immersive content delivery.
Funding is telling a similar story. XR startups raised $1.6 billion in 2024, led by Magic Leap ($590M) and Infinite Reality ($350M). Notably, enterprise-focused platforms like ArborXR used by Walmart, Pfizer and Koch are scaling rapidly after securing fresh capital to meet demand.
These developments matter because XR is quietly embedding itself into core operations such as training, remote assistance, design and logistics. As XR moves from experimental to enterprise-essential, the question shifts from Will it work? to How quickly can we scale it?
This report maps the evolution of XR from 2006 to 2025 through patent trends, leading companies, top R&D centers and top inventors to spotlight where the technology is gaining ground, who’s driving innovation and what it means for strategic decision-makers in a world that’s rapidly moving beyond the screen.
How many patents were filed in Extended Reality (XR) Industry?
This chart presents the annual trend in global XR-related patent filings from 2006 to 2025. It tracks the total number of patents filed each year across the XR ecosystem.
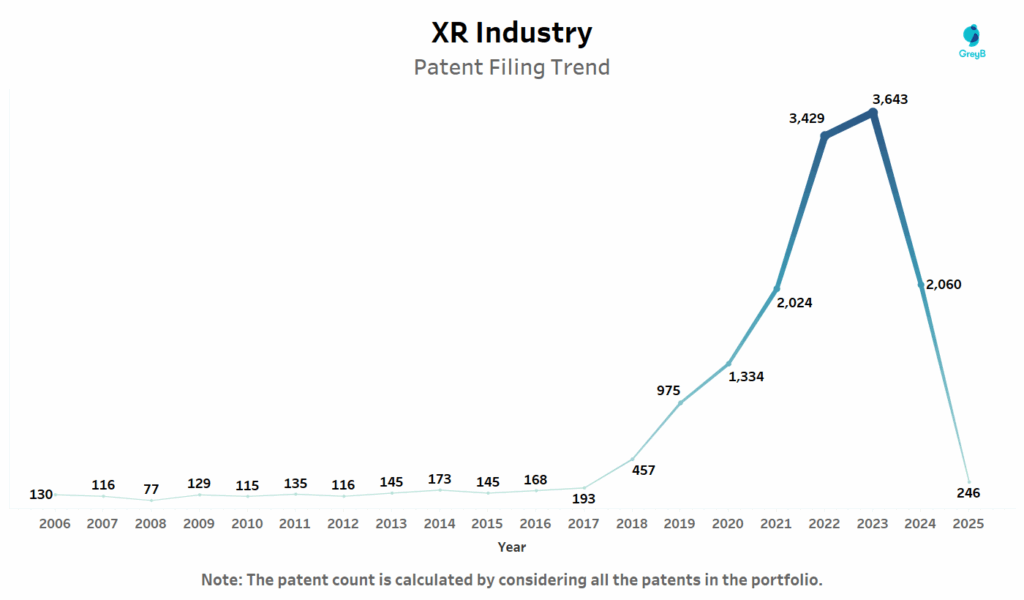
XR innovation didn’t explode overnight it simmered for a decade before erupting between 2018 and 2023, driven by breakthroughs in spatial computing, AI-driven interfaces and enterprise adoption. Patent filings surged over 700% between 2017 and 2023 reflecting a global race to secure core IP across use cases like immersive training, AR logistics and digital twins.
But in 2024, filings appear to retreat sharply. Is innovation slowing down? Not necessarily.
Patent publication typically lags behind filings by 18 months, meaning that many of the 2024–2025 inventions may simply not be visible yet. We are comparing the most recent published records, which might not capture the full extent of 2024 and 2025 filings just yet leading to dip in patent filing trend.
While understanding filing trends offers a glimpse into R&D momentum, it’s equally important to know how long these innovations take to materialize into granted IP rights. The next insight explores the grant timeline an essential metric for evaluating patent office efficiency and gauging how quickly XR innovations secure protection.
How Fast Are Extended Reality (XR) Patents Granted?
This chart breaks down how long XR-related patents typically take to receive a grant after filing.
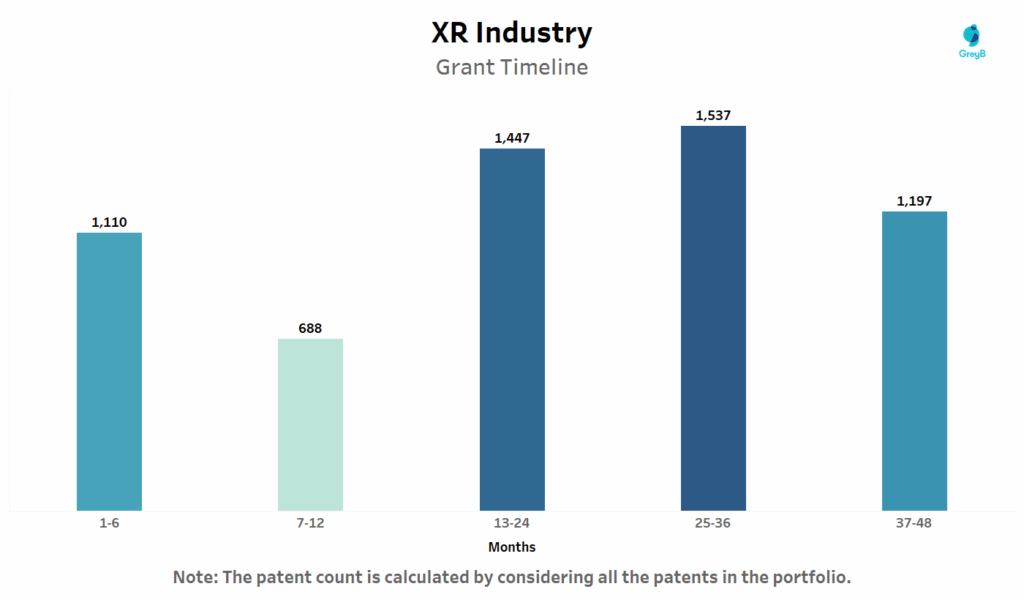
The highest volume of grants falls in the 25–36 month window closely followed by 13–24 months. Surprisingly, over 1,100 patents were granted in just 1–6 months, suggesting either accelerated examination pathways or continuation/divisional filings of previously examined cases.
However, nearly 1,200 patents took 37–48 months to grant, reflecting that a significant share of XR patents still face extended prosecution timelines. These patterns underscore the need for strategic filing and possible fast-track options when time-to-market is critical especially in a fast-evolving field like Extended Reality.
To truly understand where XR innovation is concentrated, we need to zoom out and map which countries are shaping the IP landscape and how their innovation strategies compare.
Which Countries Are Shaping the Global XR Patent Landscape?
This map visualizes the geographic distribution of XR patent filings across key countries.
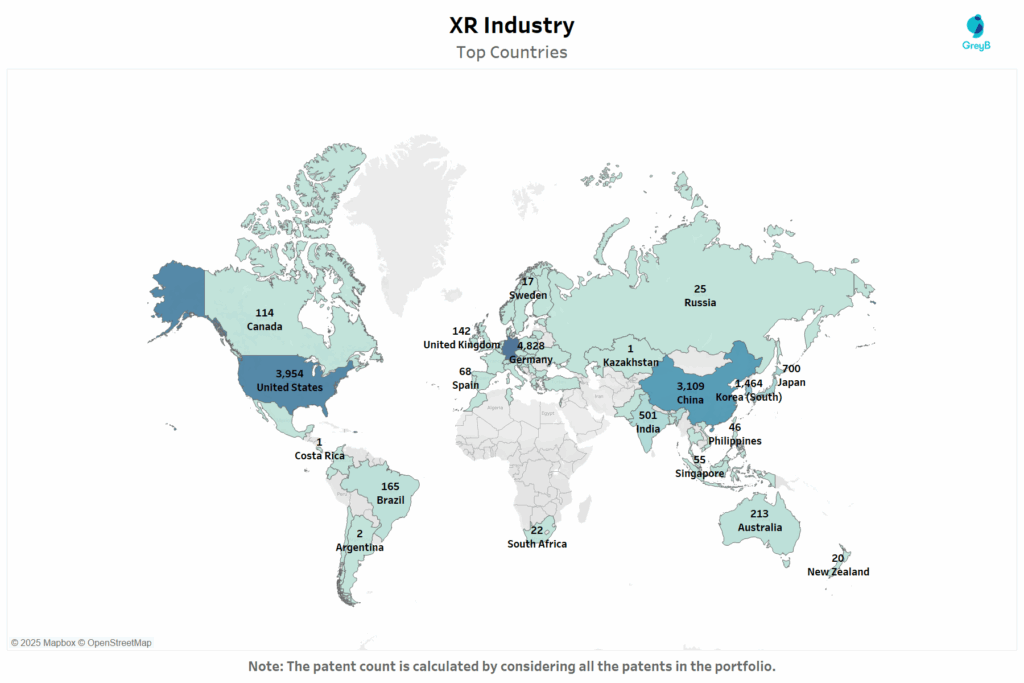
The global surge in XR patents reflects a strategic mix of scale, specialization and industrial policy. The US leads in foundational platforms leveraging corporate R&D from giants like Apple and Meta while China focuses its filings on AR hardware, smart glasses and XR-cloud synergies tied to its smart-city ambitions.
South Korea and Japan, known for their optics and semiconductor strengths, are filing heavily in lens tech, gesture tracking and display innovation, underscoring hardware-first design philosophies.
Germany’s presence signals momentum in industrial XR where Siemens, Bosch and automotive OEMs are embedding AR for maintenance and quality assurance. Meanwhile, India and Australia show growth aligned with government-backed innovation in healthcare, education and enterprise XR capabilities.
However, the real engine of XR innovation lies in the physical R&D centers powering prototypes, experiments, and testbeds worldwide. Let’s now explore where these labs and innovation hubs are concentrated.
Where Are XR R&D Centers Concentrated Across the Globe?
This map visualizes the number of XR-related R&D centers worldwide, represented by the count of unique patent families which is a strong indicator of active innovation labs and research units.
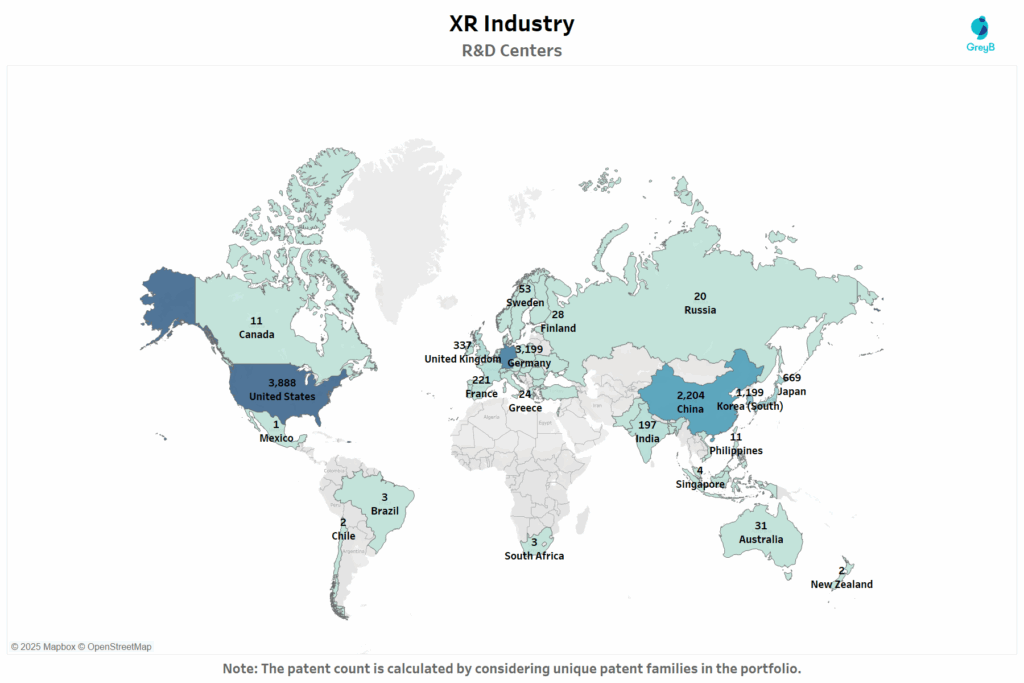
While patent volume shows who’s participating, this chart reveals where XR is actually being built. The United States dominates with innovation hubs spread across Silicon Valley, Boston, and Austin which house research labs by Apple, Meta and Microsoft.
China’s 2,204 filings are backed by provincial tech parks and national funding, including the development of metaverse-oriented XR in cities like Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen. Its Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) announced plans to grow 100 key VR enterprises by 2026.
Germany stands out with R&D centers with firms like Siemens and Bosch deeply invested in factory-floor XR. Meanwhile, Japan and South Korea continue pushing optics, semiconductors, and gesture-driven XR interfaces via corporate labs run by Sony, Samsung and LG.
Now that we know where XR is being developed, let’s explore types of intellectual property in the XR Industry whether it’s patents, patent applications or design patents.
What Types of Patents are Driving XR Industry?
This pie chart illustrates the composition of patent filings in the XR industry. This breakdown reveals how innovation in XR is primarily protected through technical IP (patents and applications), with minimal emphasis on industrial design filings.
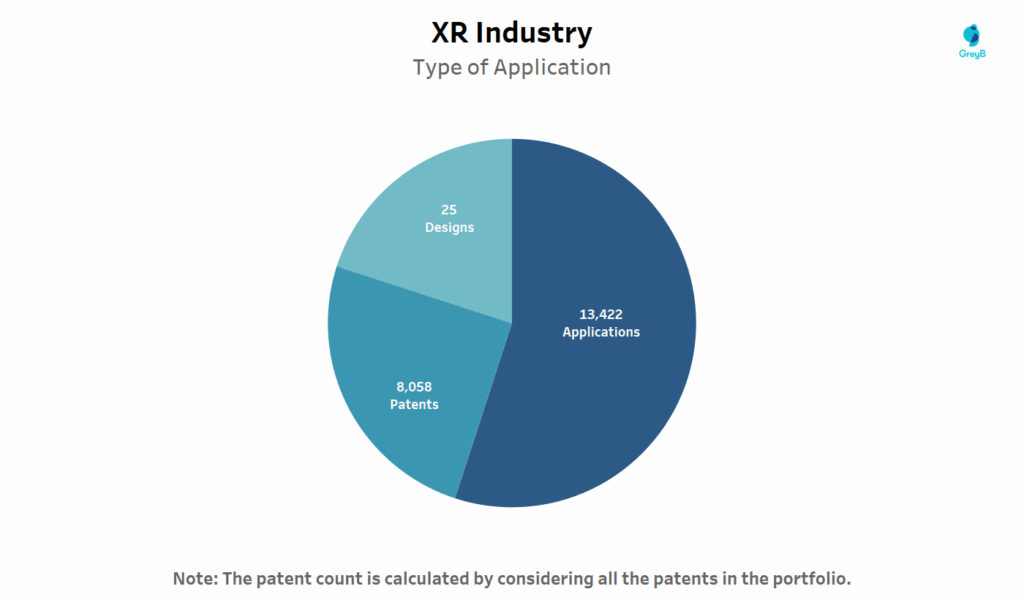
The dominance of pending applications (over 60% of all filings) shows that XR is still a fast-moving, evolving technology space with many inventions yet to mature into granted rights. This trend reflects companies racing to file early and staking claims on sensor fusion, spatial mapping, AI-driven interaction, and hardware miniaturization.
The relatively low share of design patents just 25 suggests that while form factor matters, XR innovation is currently more focused on the “how” than the “look.” In other words, function is leading form, as R&D efforts center around solving technical challenges like field-of-view stabilization, latency and real-time rendering.
This brings us to the next question, how much of this intellectual property remains relevant today? To answer that, let’s explore the split between active and inactive patents in the XR patent landscape.
How many Extended Reality (XR) Patents are Active and Inactive?
This chart shows the patent legal status of patents in the XR industry.
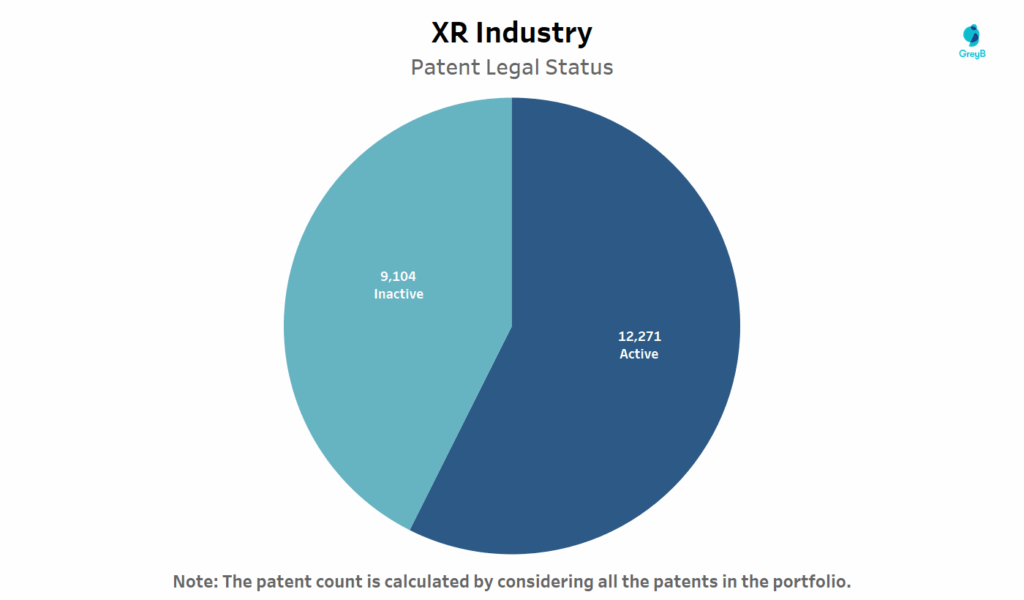
More than half of XR-related patents are still legally active (57%) which is a strong indicator that the technology is in its commercialization window. The active filings cover core areas like spatial computing, 3D sensing, real-time rendering and multi-user interactions.
So how long will this IP remain relevant? The next section breaks down the remaining life span of XR patents, giving us a clearer picture of how long companies can expect to benefit from their filings.
How Much Life Does Extended Reality (XR) Industry’s Patent Portfolio Really Have?
This chart illustrates the remaining life of active XR patents, segmented into year blocks. This distribution highlights the long-term enforceability and licensing potential of XR Industry’s current IP landscape.
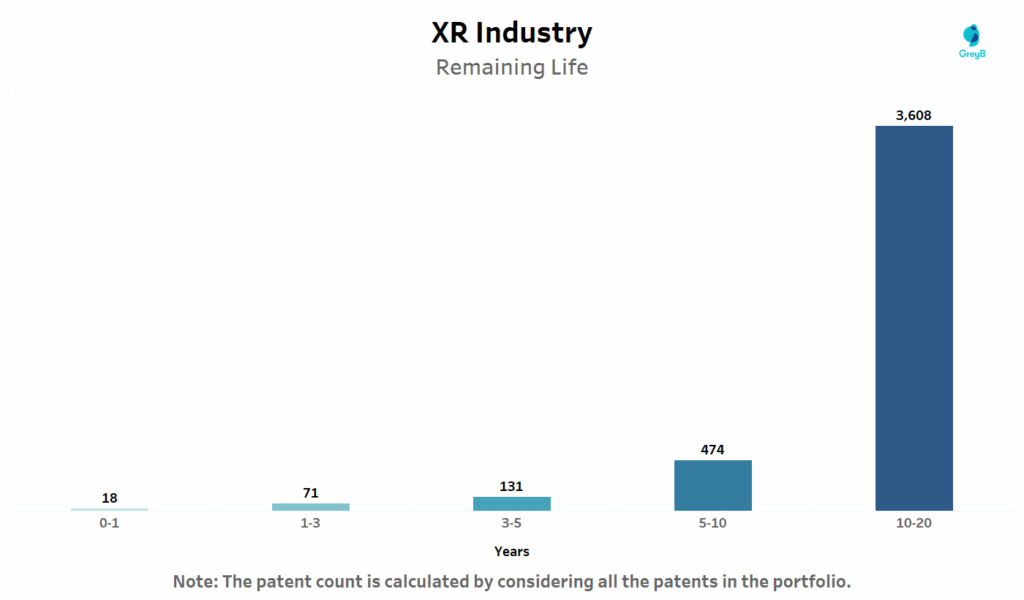
The XR industry is still building its foundations and this chart proves it. Over 80% of enforceable XR patents have more than five years of life left, giving companies ample time to commercialize, license or litigate their innovations. It’s a sign that most of this IP was filed recently, riding the post-2017 innovation wave we saw earlier.
This is also a green flag for investors and acquirers: portfolios heavy on 10–20-year runway suggest long-term asset value, which is essential in tech areas where products evolve but the enabling IP remains core (e.g., tracking systems, XR input devices, or AI-based object recognition).
However, lifespan alone doesn’t determine value. Next, let’s uncover which XR patents are most cited by others and what they reveal about the foundational innovations shaping this space.
Which Are the Most Cited Patents in Extended Reality (XR) Industry?
This chart highlights the most cited patents in the XR industry those referenced most frequently by later filings. High citation counts signal a patent’s influence in shaping core XR technologies and its relevance across evolving applications.
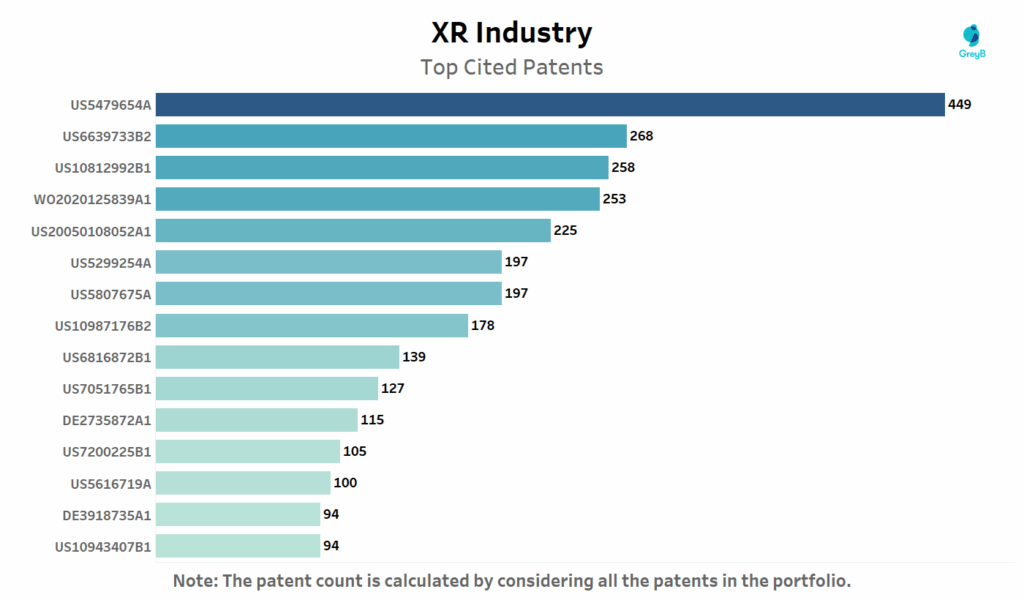
So who’s behind these foundational inventions? Up next, we spotlight the companies filing and owning the most XR patents, revealing who’s truly steering the industry forward.
Which Are the Top Companies in the Extended Reality (XR) Industry?
This chart ranks companies by their total number of XR-related patents.
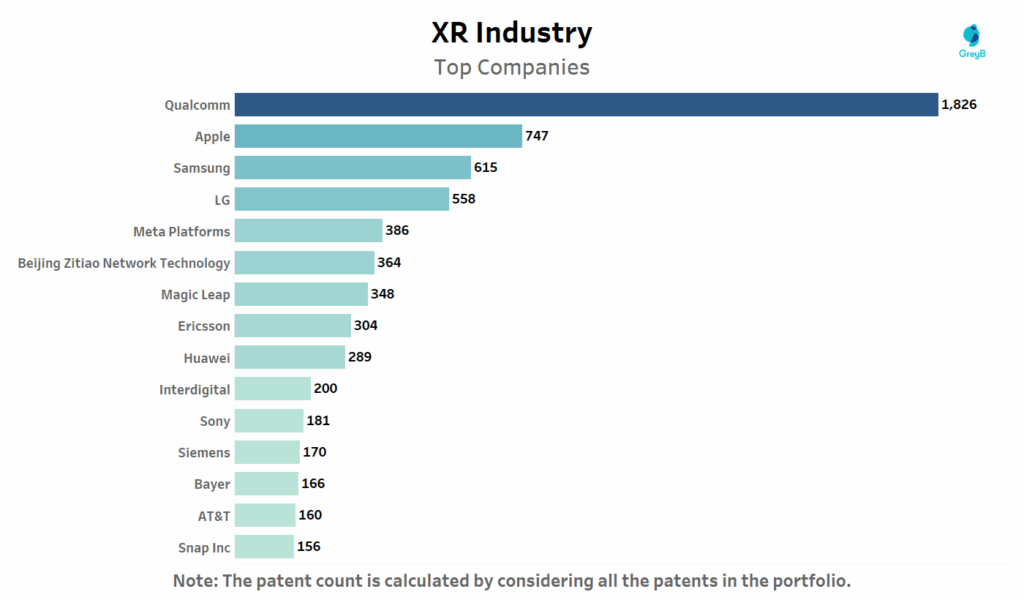
Qualcomm’s lead in XR patents reflects its role as the backbone of spatial computing owning core technologies in chipsets, sensor fusion, wireless protocols and thermal optimization for head-worn devices. Its Snapdragon XR platforms now power most commercial VR/AR headsets, including Meta’s Quest and Microsoft’s HoloLens.
Apple, with 747 patents, is catching up fast especially since the launch of its Vision Pro headset, which integrates eye-tracking, gesture control and an entirely spatial UI. Many of Apple’s patents focus on intuitive human-machine interaction bridging physical gestures with digital command.
Well, are these companies filing consistently, or was it just a surge during the hype cycle? The next chart tracks how the patenting activity of these XR leaders has evolved over time.
How Have Leading XR Companies Shifted Their Patent Strategies Over Time?
This chart shows the yearly filing trend of XR-related patents for top companies in the industry from 2019 to 2025.
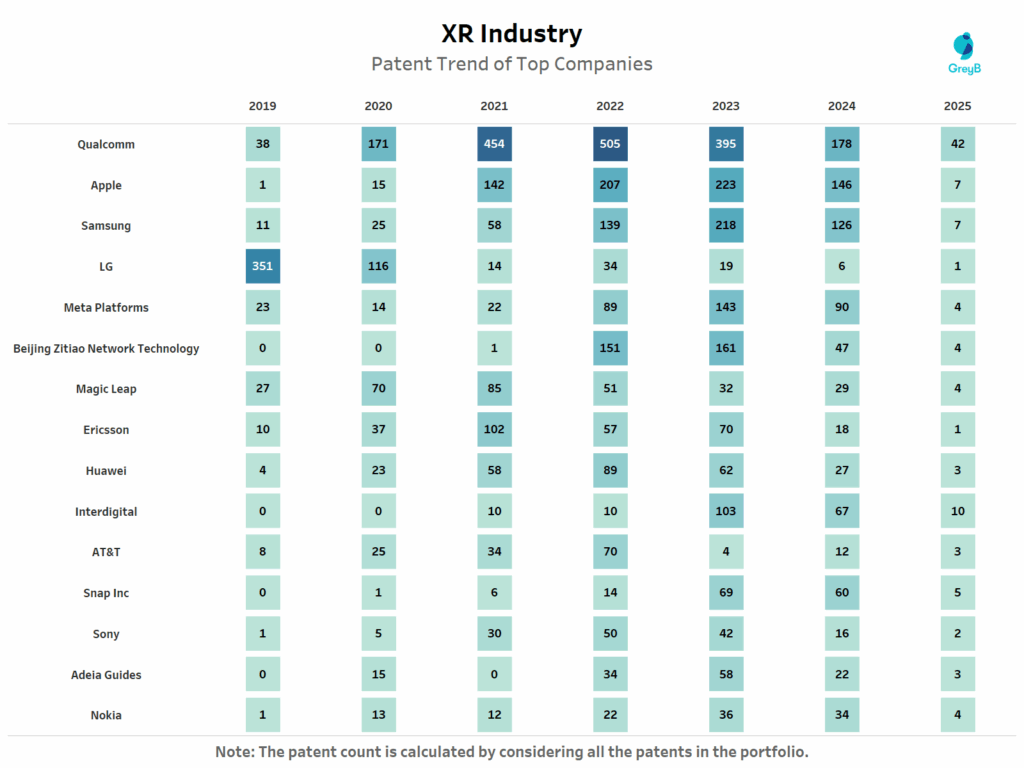
This chart reveals a strategic shift in XR innovation. LG’s early dominance in 2019 has since faded, while Qualcomm scaled aggressively between 2020 and 2022, aligning with its XR2 chip platform releases. Apple and Meta ramped up filings after 2020, reflecting deep investment in Vision Pro and Meta Quest ecosystems.
Interestingly, Beijing Zitao, owned by ByteDance barely existed in the IP landscape until 2021 yet filed more XR patents than Google in 2023, signaling the rise of AI-powered immersive content and TikTok’s foray into wearable tech.
Interdigital, long a silent IP player, shows a steady uptick post-2021, suggesting licensing-focused filings in XR communications and compression protocols. Meanwhile, consistent drops across multiple companies in 2024–25 likely reflect the patent publication lag and strategic refocusing amid economic tightening and AI convergence.
Now that we’ve seen who’s filing the most, let’s spotlight the minds behind the innovation the top inventors driving XR breakthroughs across industries.
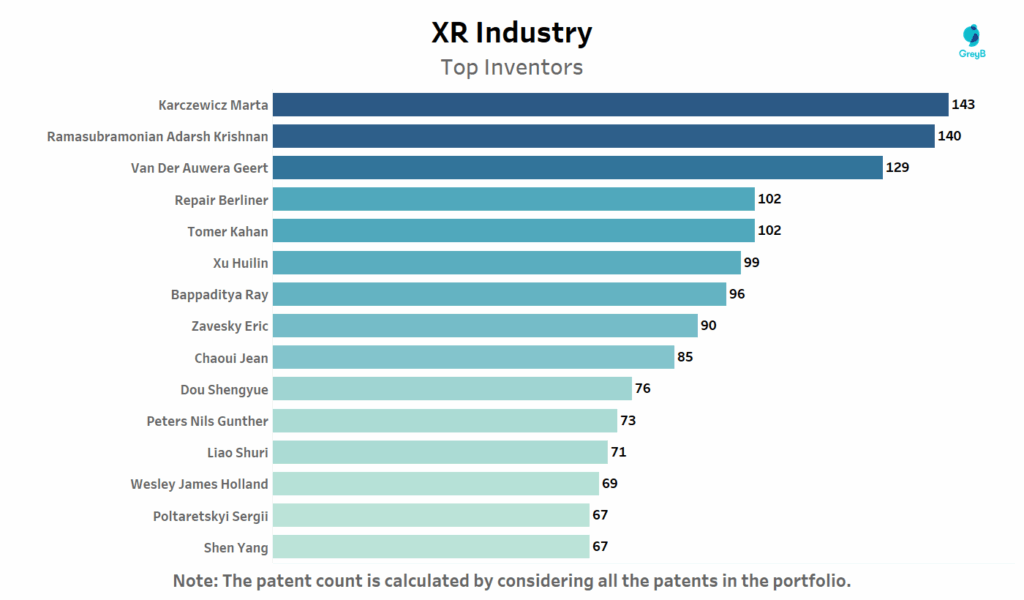
Who Are the Top Inventors behind Extended Reality (XR) Patents?
This chart ranks inventors by the number of XR-related patents they’ve contributed to.
When exactly have these inventors been most active? Let’s examine their patenting patterns across the last six years to uncover how their innovation trajectories have evolved with XR’s rise.
How Has the Patent Filing Trend of Top XR Inventors Evolved?
This chart tracks the annual patent filing activity of leading XR inventors from 2019 to 2025.
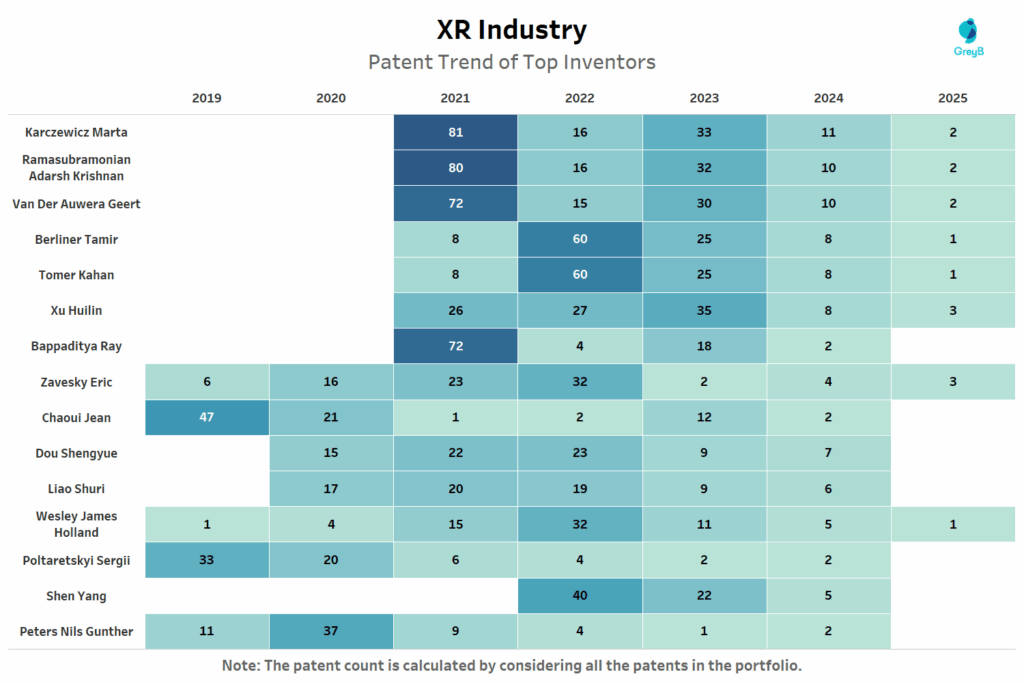
This filing timeline paints a clear picture: the peak years of individual innovation in XR were between 2020 and 2022, when spatial computing, edge AI, and sensor miniaturization matured together. Leaders like Karczewicz, Krishnan and Geert collectively filed hundreds of patents during this window laying the foundation for platform-ready XR systems that now power devices like Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest.
Notably, inventor activity dips post-2023, likely due to publication lag but it also suggests that many have shifted from IP generation to optimization and integration with AI/ML modelsfor enhanced contextual computing.
With this, let’s shift our focus towards what exactly are these inventors building? In the next chart, we break down their patents by technology domains, revealing the technical core of XR’s most prolific minds.
Which Key Technology Areas are Top XR Inventors Focusing On?
This heatmap displays the technological focus areas of top XR inventors, based on their patent filings.
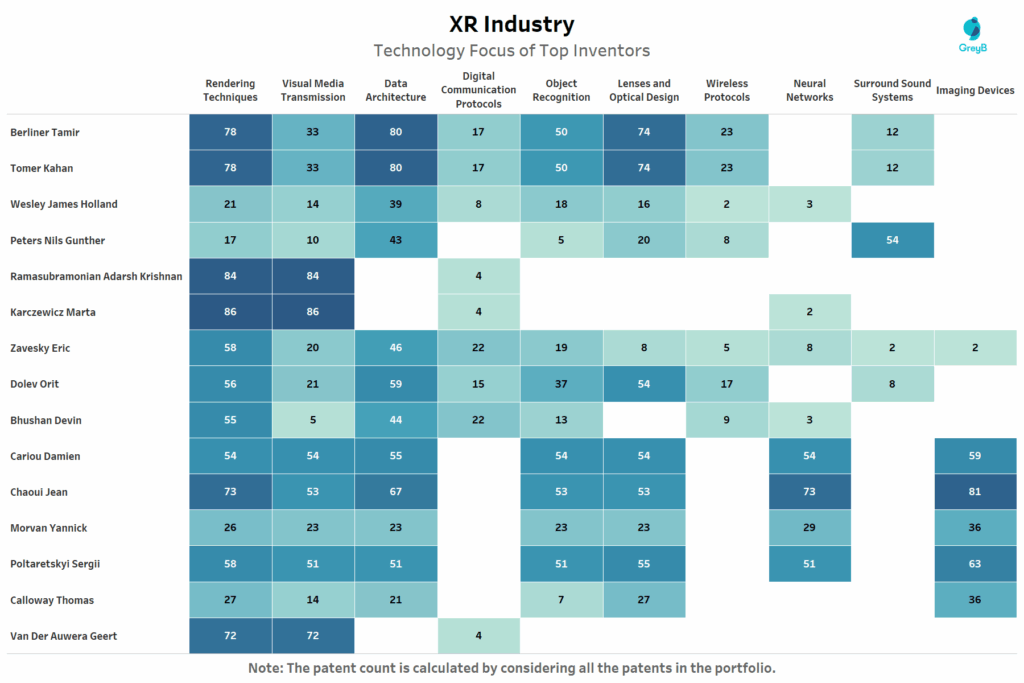
This map of innovation reveals two distinct archetypes: platform architects and technical specialists. On one end, inventors like Karczewicz Marta, Ramasubramonian Adarsh Krishnan and Van Der Auwera Geert dominate across rendering, visual transmission and compression the invisible plumbing behind high-fidelity, low-latency XR.
On the other hand, Chaoui Jean, Cariou Damien and Poltaretskyi Sergii show deep concentration in neural networks, imaging devices and surround sound indicative of immersive experience designers optimizing how XR systems sense, hear and interpret the world. Inventors like Zavesky Eric and Bhushan Devin straddle both realms, contributing to core processing as well as real-time interface responsiveness.
This split underscores XR’s complexity: innovation doesn’t just happen at the device or app level it’s built across network protocols, spatial acoustics and perceptual AI. And each of these top inventors is helping construct a different layer of that stack.
Now that we’ve seen which technologies dominate the portfolios of individual inventors, let’s zoom out to uncover which tech areas are leading the XR industry.
Which Key Technology Areas are dominating the Extended Reality (XR) Industry?
This chart displays the leading technology areas in the XR patent landscape by volume.
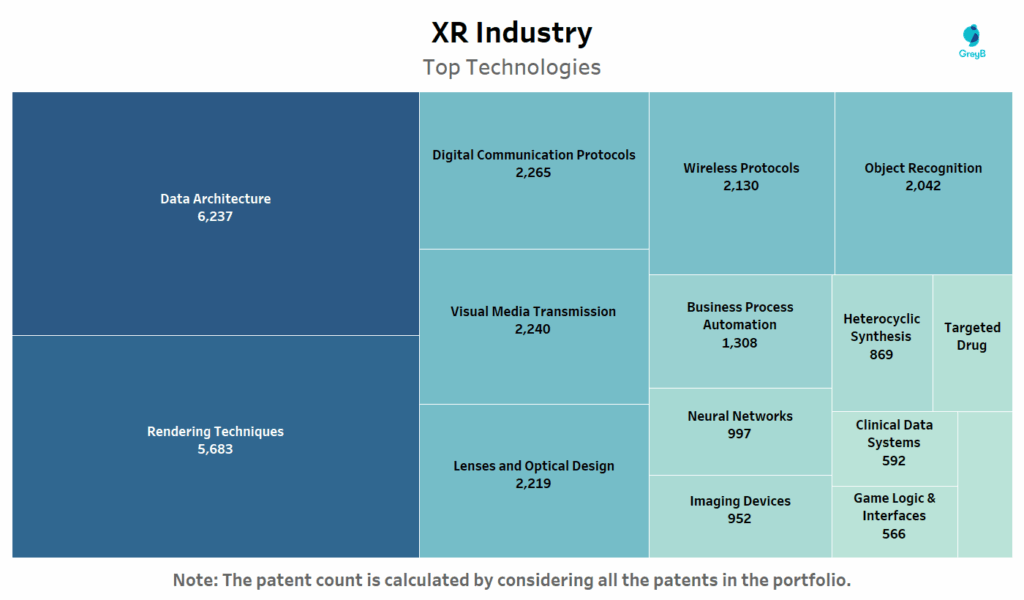
XR’s patent landscape is shaped less by flashy features and more by core enablers that make immersive experiences fast, fluid and believable. The dominance of Data Architecture reflects the growing need for real-time sensor integration, spatial memory and cloud synchronization across XR environments.
Rendering Techniques are essential to delivering high-fidelity visuals without motion lag, especially in head-mounted displays. Technologies like foveated rendering and AI-based scene prediction have become critical for user comfort and energy efficiency.
Similarly, the high patent volume in Digital Communication Protocols and Wireless Systems shows just how reliant XR has become on low-latency connectivity, especially with the rise of edge computing and 5G. Meanwhile, Visual Media Transmission and Optical Design highlight efforts to enhance clarity and reduce eye strain areas where firms like Sony, Samsung and Meta have invested heavily.
Here’s a quick snapshot of the most strategic domains:
| Leading Tech Area | Patent Volume | Why It Matters |
| Data Architecture | 6,237 | Powers real-time data handling for immersive tools |
| Rendering Techniques | 5,683 | Visual engine behind AR/VR/MR environments |
| Digital Protocols | 2,265 | Ensures XR works smoothly across devices |
| Visual Media & Optics | ~2,200+ each | Enhances clarity, realism, and device UX |
To see how these technologies have evolved in focus over time, let’s explore how patent activity has shifted across different technical domains from 2019 to 2025 and what that tells us about the future of XR.
How Have XR Technology Priorities Shifted from 2019 to 2025?
This chart tracks the annual patent filing volumes across top XR technology domains from 2019 to 2025.
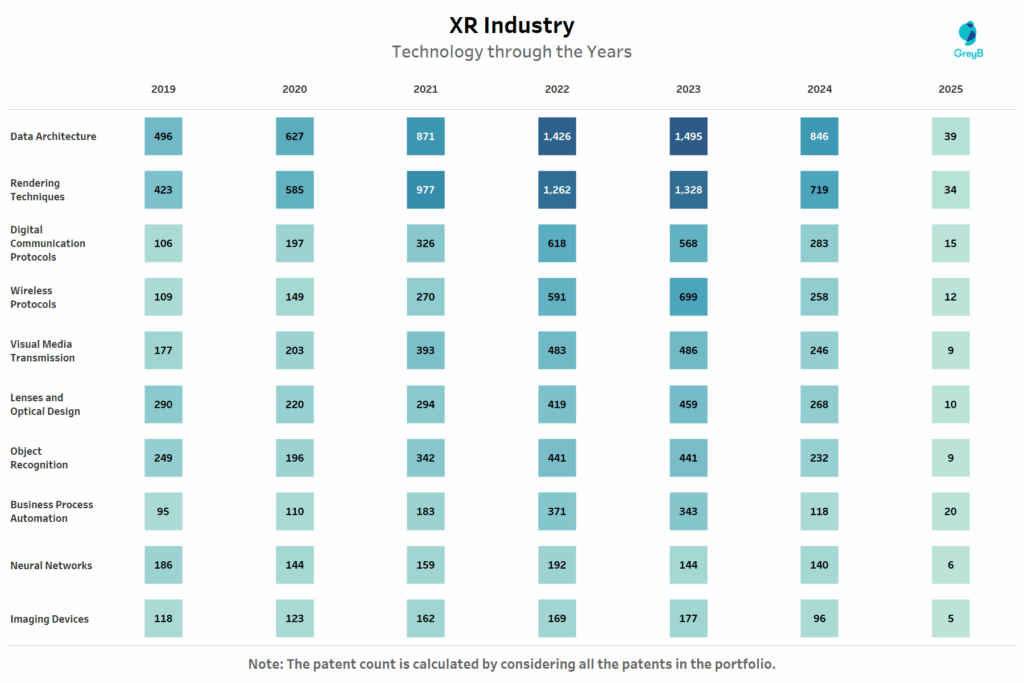
Between 2019 and 2023, XR patenting surged across nearly every tech area. The sharp rise in Data Architecture and Rendering Techniques reflects industry-wide demand for real-time, high-fidelity spatial computing. These were foundational years for enabling smoother XR experiences as headsets became more lightweight, network-connected and enterprise-ready.
Other technologies like Digital Communication Protocols, Wireless Systems and Optical Design followed similar upward arcs supporting the integration of XR into remote collaboration, digital twin environments and immersive industrial workflows.
However, post-2023, nearly all categories show a visible decline a pattern likely explained by a combination of:
- Patent publication lag (2024–2025 filings not fully visible yet),
- A shift toward consolidation and refinement rather than new IP generation, and
- The growing intersection of XR with AI, where innovation is being filed under hybrid categories.
The decline isn’t a signal of stagnation it’s a sign that XR is moving out of experimentation and into execution. Core infrastructure has been established; now, the focus is on scaling, integrating and applying it across industries.
As innovation in XR technologies accelerated year after year, another trend quietly emerged in the background one that often shadows technological breakthroughs: litigation.
How Has the Litigation Activity in XR Industry Changed?
This chart maps the timeline of patent litigations in the XR industry from 2009 to 2025.

Just as technology in XR took a sharp upward curve, so did the legal heat. The litigation timeline reveals a quiet decade followed by a sudden rise in patent disputes peaking in 2021 with five litigations, then tapering slightly before ticking upward again in 2024 and 2025. This pattern suggests that as XR technologies matured and commercial stakes increased, so did the friction over intellectual property.
In many ways, this timeline mirrors the lifecycle of a tech revolution: initial innovation, rapid adoption, followed by legal battles over ownership and implementation. The recent uptick in 2024–2025 could hint at the emergence of competitive overlaps, signaling the need for stronger IP strategy and defensive patenting.
Looking for detailed patent insights in a specific XR Industry area?
Submit your interest, and our team will reach out to explore a customized report for you!


