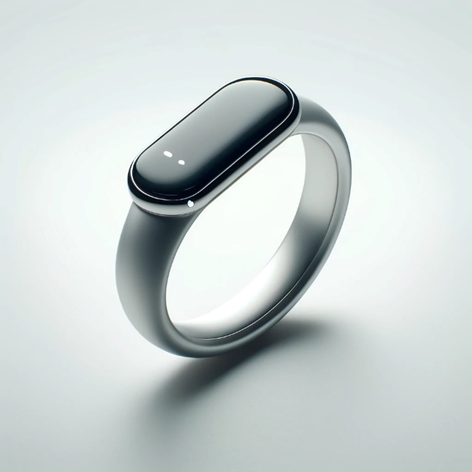
Apple is set to expand its wearable technology lineup with the introduction of the Apple Ring, a device poised to offer more than just health tracking. Recent patents indicate the ring will integrate with Apple’s existing products, allowing users to manage their devices with simple gestures. This integration promises to streamline how we interact with technology, making it both more accessible and efficient. The Apple Ring is expected to feature health monitoring, NFC capabilities, and a design that meets Apple’s high standards of aesthetics and functionality. With its launch, Apple aims to transform everyday convenience for its users.
The innovation behind the Apple Smart Ring
We’ve analyzed key patents related to Apple Ring. Read the summary below and discover the ingenious innovations behind this breakthrough technology!
How does the Apple Smart Ring Function?
Health Tracking: It will monitor heart rate, respiratory rate, and sleep quality using embedded sensors.
Gesture Recognition: Users can control other Apple devices through hand gestures.
Ecosystem Integration: The ring will seamlessly connect with Apple products like iPhones and Macs via wireless technologies.
NFC for Payments: Incorporates NFC to enable contactless payments through Apple Pay.
Premium Design: Focus on stylish, durable, and comfortable wearability.
Efficient Battery Use: Designed for extended battery life due to minimal display requirements and efficient power management.
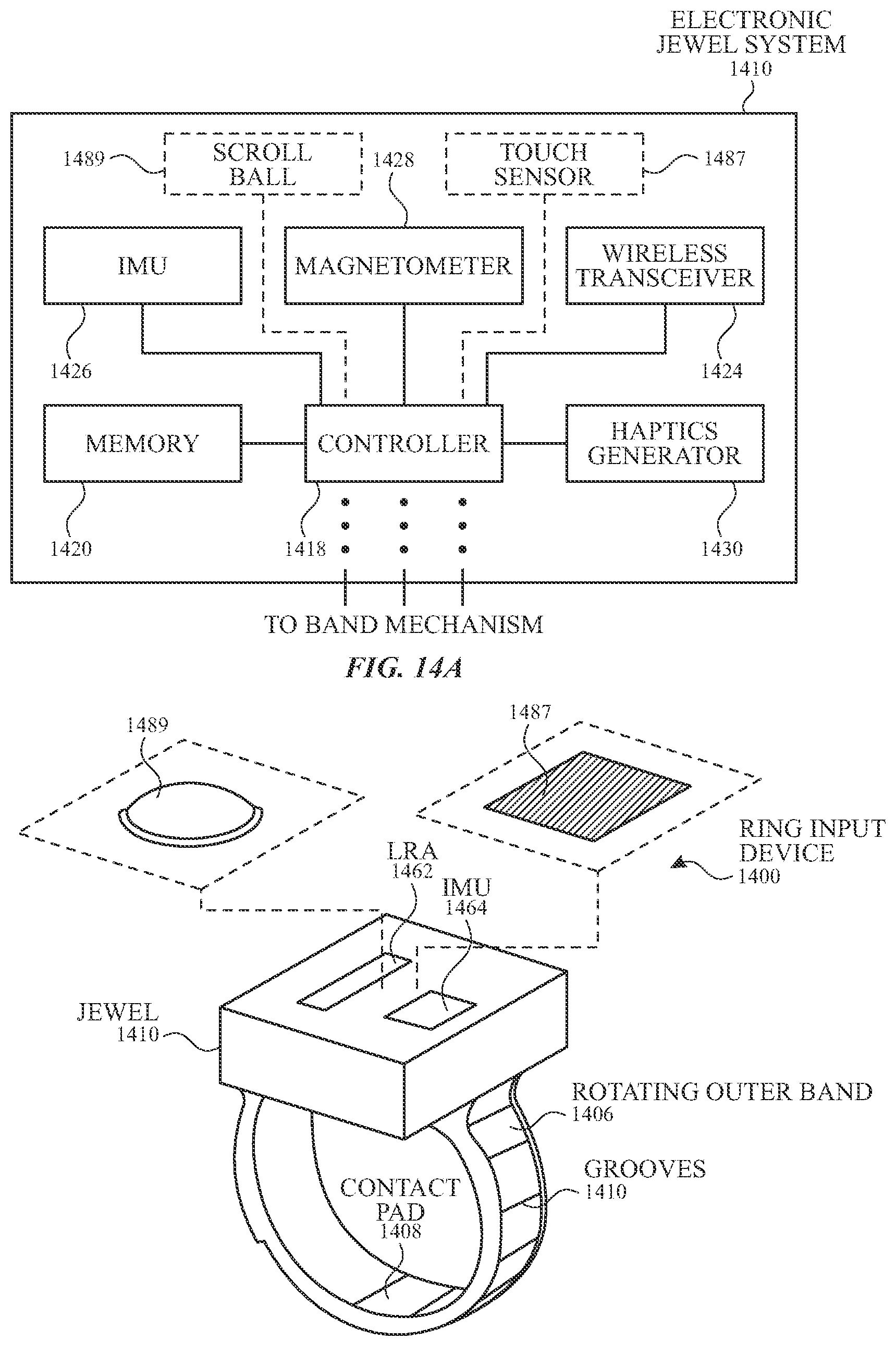
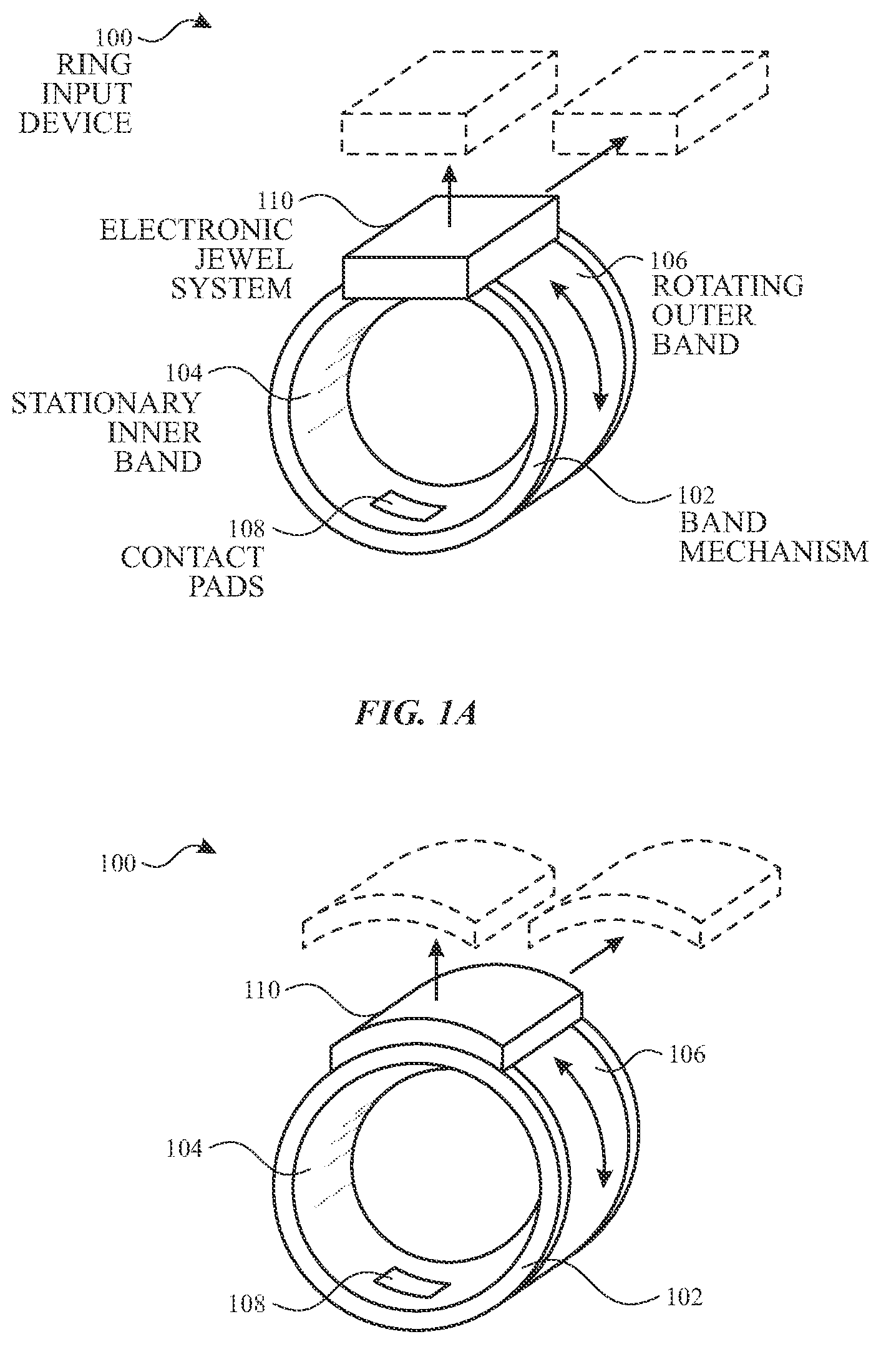
The patent US11971746B2 outlines a smart ring that allows users to control electronic devices via touch and force sensors. This ring, which can wirelessly transmit commands to connected devices, also provides haptic feedback and features an adjustable design to fit various finger sizes. This integration of convenience and technology offers a new way to interact seamlessly with electronic devices.
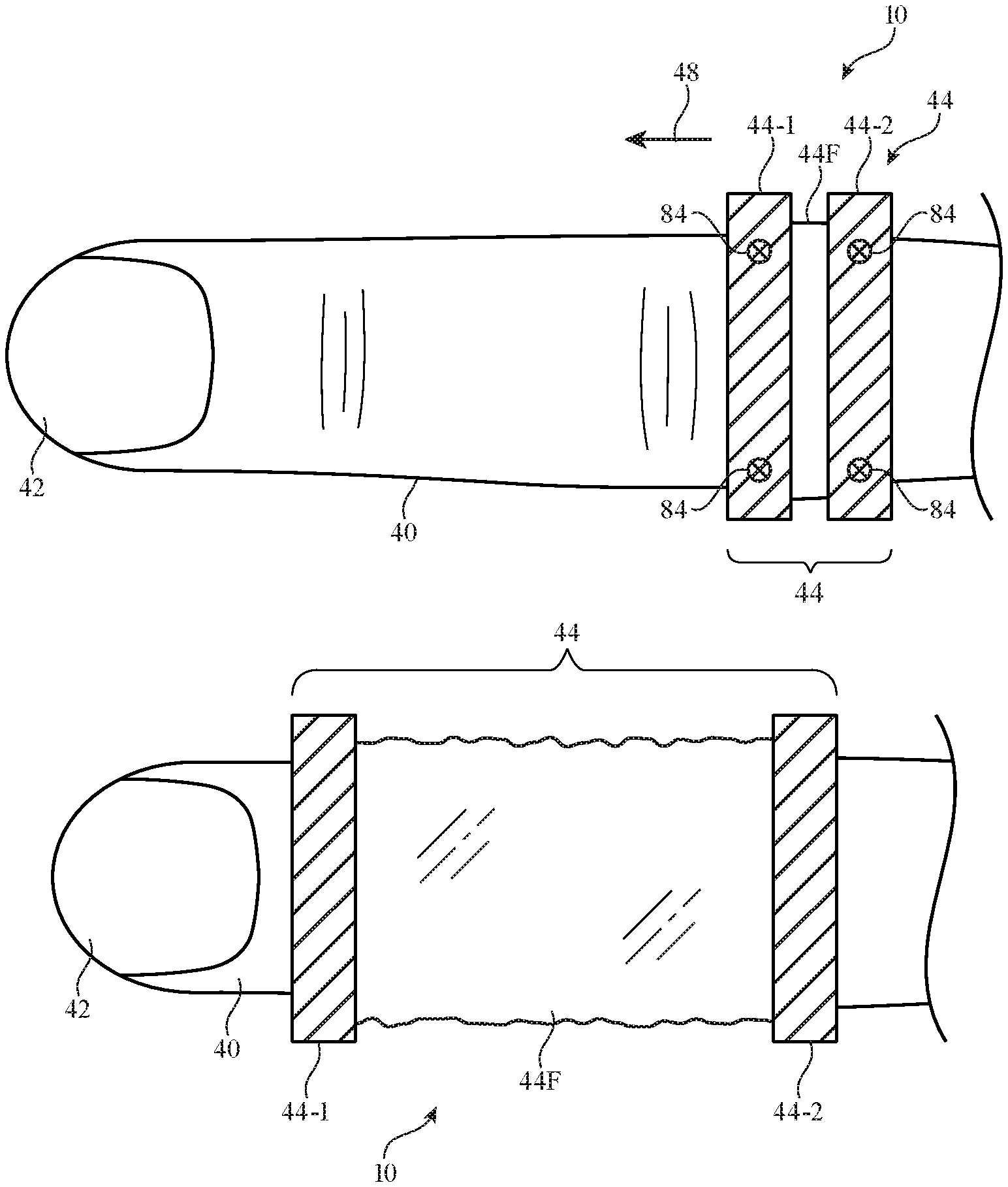
The patent US11733790B2 about a type of ring that can detect pressure on its surface, allowing it to perform various actions wirelessly with other devices. These rings are designed to be small and inconspicuous, making them ideal for discreet communication or controlling other devices. While they’re mostly discussed as finger rings, they can also be part of necklaces, earrings, bracelets, or even toe rings. The key is their ability to sense pressure and translate that into wireless commands for different purposes.
These smart rings let you control devices without using your hands. They’re discreet and useful for people with limited mobility, and they work well with smart gadgets like lights or games.
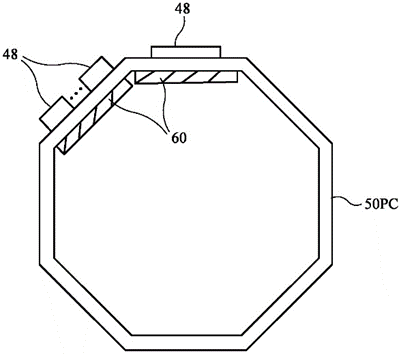
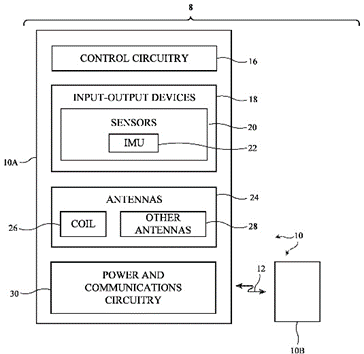
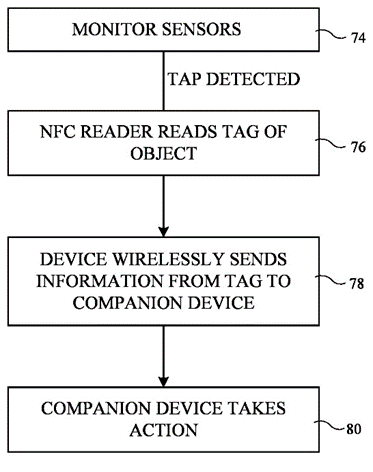
The patent US11829831B1 describes a wearable electronic device designed to be worn like a ring on a user’s finger. It contains a coil made from metal traces on a circuit board that wraps around the ring. The device can read information from nearby tags using near-field communication (NFC) technology when the user interacts with it. It also has wireless technology to send this tag information and user inputs to another device, like a smartphone or computer.
This patent allows a ring to read data from NFC tags and wirelessly send it to another device. It makes data transfer quick and easy with just a touch.
This patent US10036087B2 describes a type of metallic glass made from alloys of platinum (Pt), copper (Cu), and phosphorus (P), which can also include additional elements like boron (B), silver (Ag), and gold (Au). These added elements help increase the thickness (critical rod diameter) that the alloy can achieve while still maintaining its glass-like properties. The document outlines various compositions of these alloys, specifying different ratios of Pt, Cu, and P, along with specific amounts of Ag, Au, and B to achieve desired physical properties. In simpler terms, it’s about creating a stronger and more durable type of metallic glass that can be used for making jewelry and other items by fine-tuning the mixture of these metals.
This patent addresses the challenge of creating stronger and more durable metallic glasses for jewelry. Traditional metallic glasses are limited in thickness without losing properties like strength and corrosion resistance. By adding elements such as boron, silver, and gold, the patent increases the critical rod diameter, allowing for thicker items while maintaining glass-like characteristics. This enhancement enables more robust and versatile applications, improving the quality and lifespan of metallic glass products.
As Apple prepares to potentially introduce the Apple Ring, it faces competition from established players like Oura and Motiv, who focus on health metrics. However, Apple’s smart ring could differentiate itself with its ecosystem integration, offering features like gesture control and NFC payments through Apple Pay. This integration could make the Apple Ring a transformative device in wearable technology, not only enhancing health monitoring but also simplifying digital interactions and financial transactions, setting a new benchmark for how wearables can enhance both digital and physical aspects of our lives.
Competitors of Apple in similar products and technology
Several companies are also developing smart rings similar to Apple’s Smart Ring. Notable examples include the Oura Ring, which focuses on health and wellness tracking; Amazon’s Echo Loop, which integrates with Alexa for voice commands; the Motiv Ring, known for fitness and activity tracking; McLear’s Smart Ring for contactless payments; the Circular Ring, which provides personalized health insights; and the Xenxo S-Ring, offering a wide range of features from call management to data storage. These companies are contributing to the growing market of wearable technology that blends functionality with style.
What other companies are filing patents in the Smart Ring space? Request a patent landscape around this technology by filling out the form below: