Constellation Energy has a total of 63 patents globally, out of which 8 have been granted. Of these 63 patents, more than 69% patents are active. United States of America is where Constellation Energy has filed the maximum number of patents, followed by Australia and Japan. Parallelly, United States of America seems to be the main focused R&D center and is also the origin country of Constellation Energy.
Constellation Energy was founded in the year 2021 after splitting off from parent Exelon. Company is doing business in carbon-free energy. As of March 2022, Constellation Energy has a market cap of $16.91 Billion.
Do read about some of the most popular patents of Constellation Energy which have been covered by us in this article and also you can find Constellation Energy’s patents information, the worldwide patent filing activity and its patent filing trend over the years, and many other stats over Constellation Energy’s patent portfolio.
How many patents does the CEO of Constellation Energy have?
The CEO, Joseph Dominguez has 0 patents.
How many patents does Constellation Energy have?
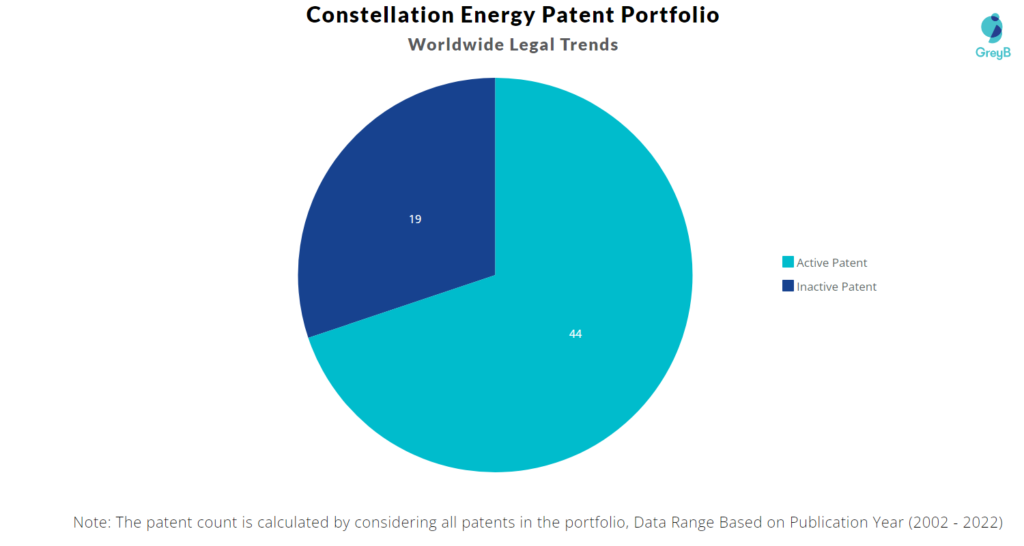
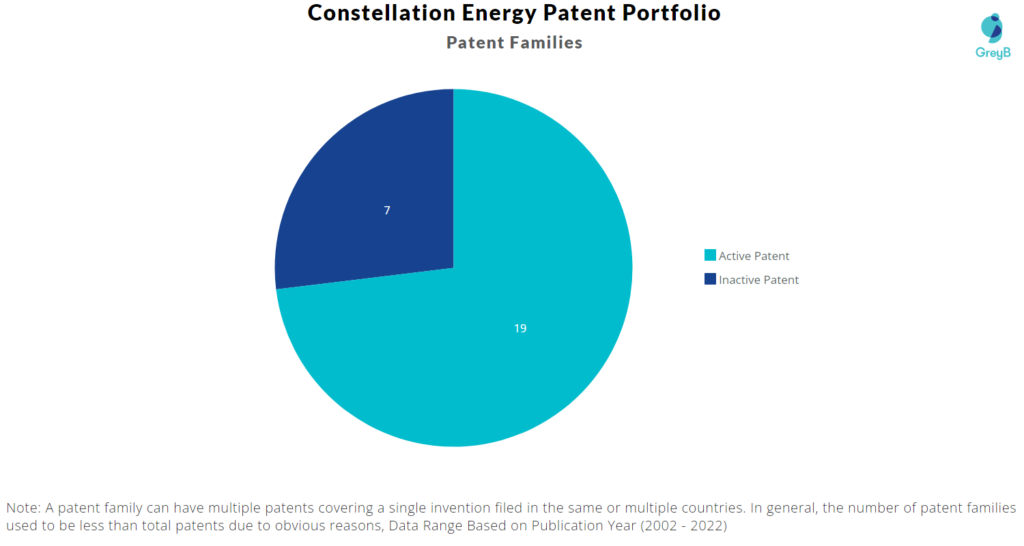
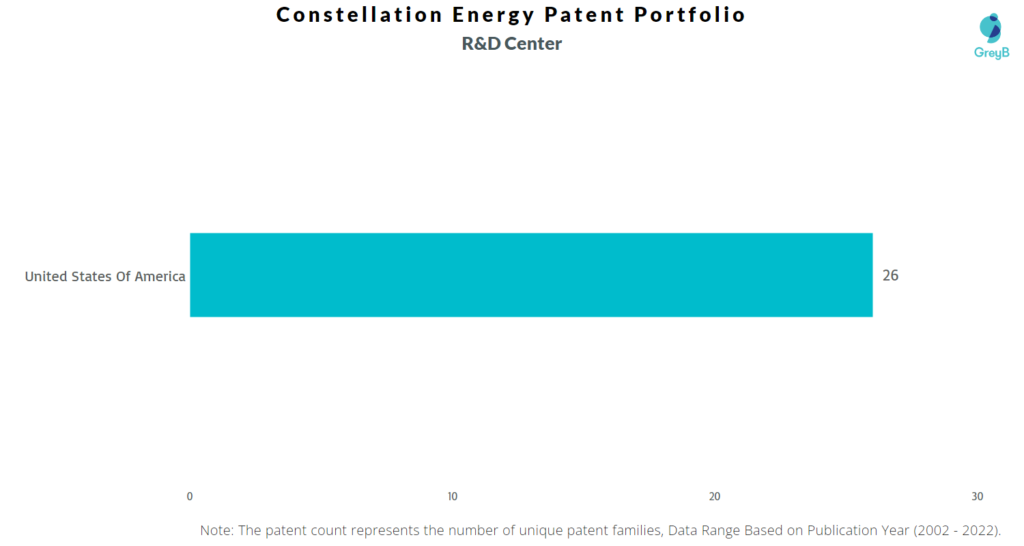
Constellation Energy has a total of 63 patents globally. These patents belong to 26 unique patent families. Out of 63 patents, 44 patents are active.
How many Constellation Energy patents are Alive/Dead?
Worldwide Patents
Patent Families
How Many Patents did Constellation Energy File Every Year?
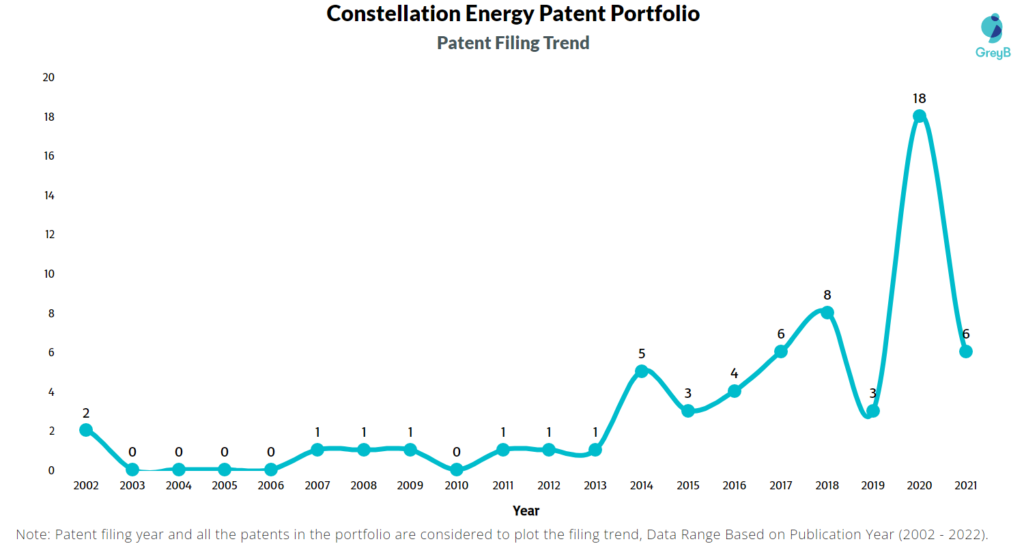
Are you wondering why there is a drop in patent filing for the last two years? It is because a patent application can take up to 18 months to get published. Certainly, it doesn’t suggest a decrease in the patent filing.
| Year of Patents Filing or Grant | Constellation Energy Applications Filed | Constellation Energy Patents Granted |
| 2011 | 1 | – |
| 2012 | 1 | – |
| 2013 | 1 | – |
| 2014 | 5 | – |
| 2015 | 3 | – |
| 2016 | 4 | – |
| 2017 | 6 | – |
| 2018 | 8 | – |
| 2019 | 3 | – |
| 2020 | 18 | 1 |
| 2021 | 6 | 1 |
How Many Patents did Constellation Energy File in Different Countries?
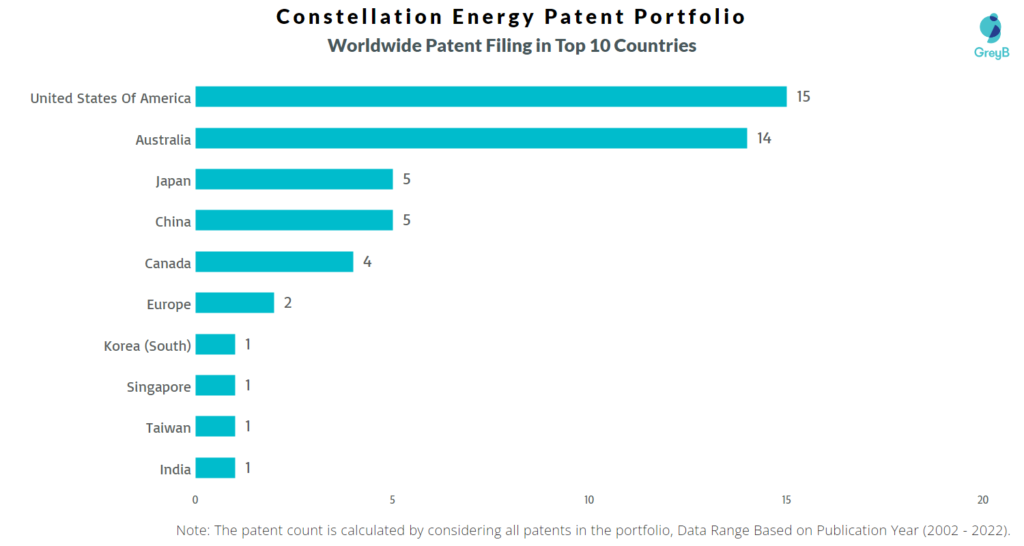
Countries in which Constellation Energy Filed Patents
| Country | Patents |
| United States Of America | 15 |
| Australia | 14 |
| Japan | 5 |
| China | 5 |
| Canada | 4 |
| Europe | 2 |
| Korea (South) | 1 |
| Singapore | 1 |
| Taiwan | 1 |
| India | 1 |
| Indonesia | 1 |
| Israel | 1 |
Where are Research Centers of Constellation Energy Patents Located?
10 Best Constellation Energy Patents
US7565227B2 is the most popular patent in the Constellation Energy portfolio. It has received 220 citations so far from companies like Honeywell, Sharp, and Consert.
Below is the list of 10 most cited patents of Constellation Energy:
| Publication Number | Citation Count |
| US7565227B2 | 220 |
| US20130084474A1 | 107 |
| US20150171455A1 | 34 |
| WO2015184252A1 | 16 |
| US20180159459A1 | 13 |
| CN107190275A | 12 |
| WO2016182605A1 | 12 |
| WO2016182600A1 | 11 |
| WO2018222569A1 | 7 |
| WO2018203953A2 | 7 |
What Percentage of Constellation Energy US Patent Applications were Granted?
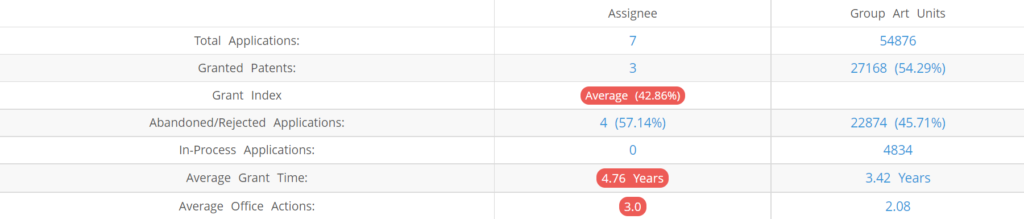
Constellation Energy (Excluding its subsidiaries) has filed 7 patent applications at USPTO so far (Excluding Design and PCT applications). Out of these 3 have been granted leading to a grant rate of 42.86%.
Below are the key stats of Constellation Energy patent prosecution at the USPTO.
Which Law Firms Filed Most US Patents for Constellation Energy?
| Law Firm | Total Application | Success Rate |
| Whiteford Taylor & Preston Llp | 5 | 40.00% |
| Davidson Berquist Jackson & Gowdey Llp | 1 | 0.00% |
List of Constellation Energy Patents
| Constellation Energy Patents | Title |
| US20220021290A1 | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| US20210359496A1 | Methods, systems, and apparatuses for transferring power and analysis |
| US20210336509A1 | Copper-Fouling-Resistant Stator Water Cooling (SWC) System and Method |
| US20210047961A1 | Power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| US20210028646A1 | Methods and systems for providing power |
| US20200103465A1 | Diagnostic lighting device |
| US20190389723A1 | Hydrogen-catalyst reactor |
| US20190188638A1 | Methods and systems for improving vehicle searches |
| US20180159459A1 | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| US9563746B2 | System and method of computing and rendering the nature of dipole moments, condensed matter, and reaction kinetics |
| US20150171455A1 | Ciht power system |
| US20130084474A1 | Electrochemical hydrogen-catalyst power system |
| US7565227B2 | Multi-building control for demand response power usage control |
| US62980959P0 | Magnetohydrodynamic electrical power generator |
| US63001761P0 | Parameters and magnetic energies due to the spin magnetic moment of h2(1/4) |
| EP3911782A2 | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| EP3114692B1 | Photovoltaic power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| CN113574206A | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| CN109247031A | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| CN107190275A | H2O-based electrochemical hydrogen-catalyst power system |
| CN106463192A | Photovoltaic power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| CN100575246C | Microwave power cell, chemical reactor and power converter |
| WO2021222402A1 | Copper-fouling resistant stator water cooling (SWC) system and method |
| WO2021159117A1 | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| WO2021016526A1 | Methods and systems for providing power |
| WO2020148709A3 | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| WO2018222569A1 | Magnetohydrodynamic electric power generator |
| WO2018203953A2 | Magnetohydrodynamic electric power generator |
| WO2017127447A9 | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| WO2018129353A1 | Extreme and deep ultraviolet photovoltaic cell |
| WO2017210204A1 | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator network |
| WO2016182600A1 | Ultraviolet electrical power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| WO2016182605A1 | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| WO2015184252A1 | Electrical power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| CA3145469A1 | Methods and systems for providing power |
| CA3124016A1 | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| CA3011972A1 | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| CA2931020A1 | Power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| AU2020200099B2 | Photovoltaic power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| AU2020209270A1 | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| AU2020277273A1 | Electrical power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| AU2020204330A1 | Power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| AU2018378300A1 | Magnetohydrodynamic electric power generator |
| AU2018261199A1 | Magnetohydrodynamic electric power generator |
| AU2018217208A1 | Power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| AU2017210155A1 | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| AU2016260177A1 | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| AU2015266760A1 | Electrical power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| AU2014385284A1 | Photovoltaic power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| AU2014351491A1 | Power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| AU2002252628B2 | Closed cycle waste combustion |
| AU733598C | Closed-cycle waste combustion |
| JP2022517816A | Electromagnetic fluid generator |
| JP2021506072A5 | Electromagnetic fluid generator |
| JP2021002523A | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| JP2019512999A | Thermophotovoltaic electrical power generator |
| JP3349705B2 | Conversion methods such as paper mill sludge |
| IN202118053459A | Photovoltaic power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| IL284722D0 | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| SG11202105967UA | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| TW202045862A | Magnetohydrodynamic hydrogen electrical power generator |
| ID201707644A | Photovoltaic power generation systems and methods regarding same |
| KR1020100017342A | Hydrogen-Catalyst Reactor |


