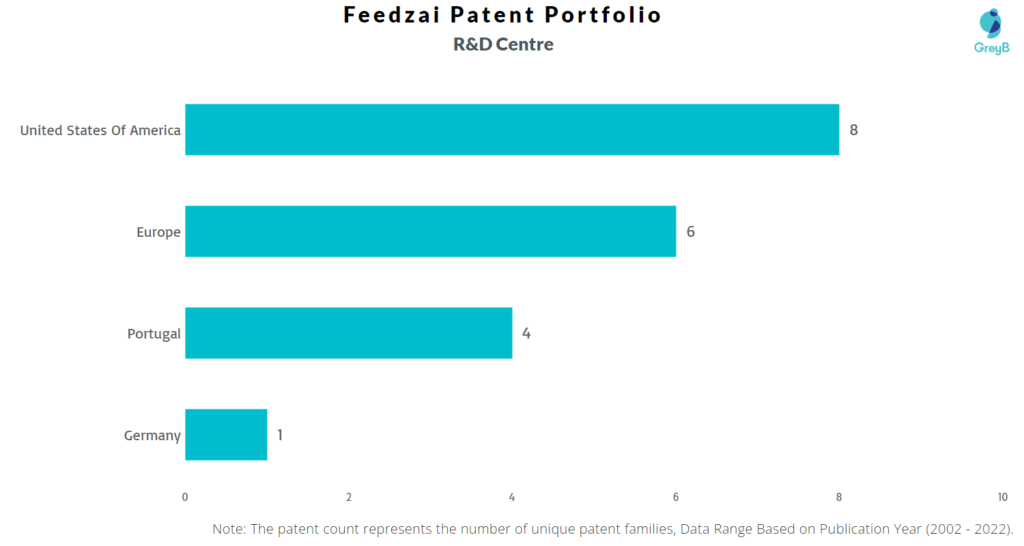
Feedzai has a total of 60 patents globally, out of which 8 have been granted. Of these 60 patents, more than 90% patents are active. The United States of America is where Feedzai has filed the maximum number of patents, followed by Europe and Singapore. Parallelly, United States of America seems to be the main focused R&D centre and also Portugal is the origin country of Feedzai.
Feedzai was founded in 2011 by Nuno Sebastiao, Pedro Bizarro and Paulo Marques. In the financial services, retail, and e-commerce sectors, Feedzai a data science business, creates real-time machine learning solutions to identify fraudulent payment transactions and reduce risk.
Do read about some of the most popular patents of Feedzai which have been covered by us in this article and also you can find Feedzai patents information, the worldwide patent filing activity and its patent filing trend over the years, and many other stats over Feedzai patent portfolio.
How many patents does the Founder and CEO of Feedzai have?
The founders and CEO Nuno Sebastiao have 0 patents, Pedro Bizarro has 68 patents and Paulo Marques have 35 patents.
How many patents does Feedzai have?
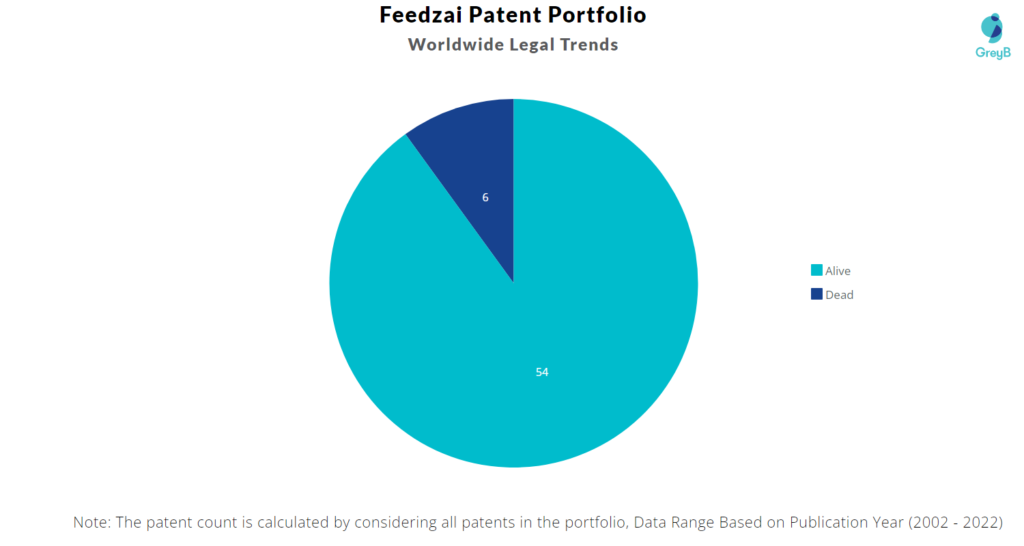
Feedzai has a total of 60 patents globally. These patents belong to 19 unique patent families. Out of 60 patents, 54 patents are active.
How Many Patents did Feedzai File Every Year?
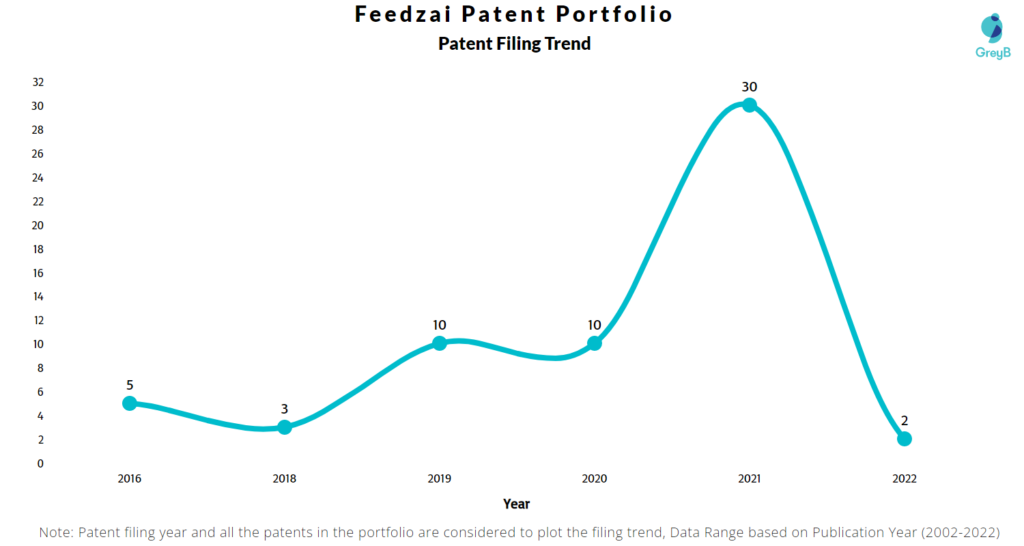
Are you wondering why there is a drop in patent filing for the last two years? It is because a patent application can take up to 18 months to get published. Certainly, it doesn’t suggest a decrease in the patent filing.
| Year of Patents Filing or Grant | Feedzai Applications Filed | Feedzai Patents Granted |
| 2016 | 5 | – |
| 2018 | 3 | – |
| 2019 | 10 | 1 |
| 2020 | 10 | 3 |
| 2021 | 30 | 1 |
| 2022 | 2 | 3 |
How many Feedzai patents are Alive/Dead?
Worldwide Patents
How Many Patents did Feedzai File in Different Countries?
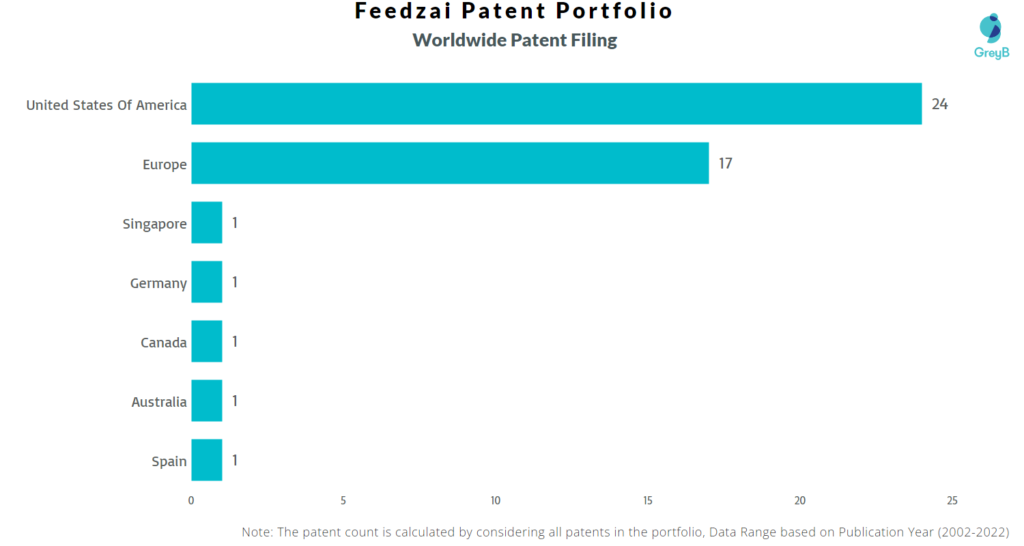
Countries in which Feedzai Filed Patents
| Country | Patents |
| United States Of America | 24 |
| Europe | 17 |
| Singapore | 1 |
| Germany | 1 |
| Canada | 1 |
| Australia | 1 |
| Spain | 1 |
Where are Research Centers of Feedzai Patents Located?
List of Feedzai Patents –
| Publication Number | Title |
| US10284590B2 | Automatic Detection Of Points Of Compromise |
| US10749892B2 | Automatic Detection Of Points Of Compromise |
| US11062316B2 | Computer Memory Management During Real-Time Fraudulent Transaction Analysis |
| US11403644B2 | Automated Rules Management System |
| US11392954B2 | Hierarchical Machine Learning Model For Performing A Decision Task And An Explanation Task |
| US11269684B1 | Distributed Streaming System Supporting Real-Time Sliding Windows |
| US20200366698A1 | Automatic Model Monitoring For Data Streams |
| US20200366699A1 | Adaptive Threshold Estimation For Streaming Data |
| US20200364586A1 | Explanation Reporting Based On Differentiation Between Items In Different Data Groups |
| US20200090003A1 | Semantic-Aware Feature Engineering |
| US20210374614A1 | Active Learning Annotation System That Does Not Require Historical Data |
| US20210248448A1 | Interleaved Sequence Recurrent Neural Networks For Fraud Detection |
| US20210124780A1 | Graph Search And Visualization For Fraudulent Transaction Analysis |
| US20210117978A1 | Graph Decomposition For Fraudulent Transaction Analysis |
| US20220245426A1 | Automatic Profile Extraction In Data Streams Using Recurrent Neural Networks |
| US20220222167A1 | Automated Feature Monitoring For Data Streams |
| US20220222670A1 | Generation Of Divergence Distributions For Automated Data Analysis |
| US20220198471A1 | Graph Traversal For Measurement Of Fraudulent Nodes |
| US20220138006A1 | Distributed Streaming System Supporting Real-Time Sliding Windows |
| US20220114494A1 | Model-Agnostic Approach To Interpreting Sequence Predictions |
| US20220114345A1 | Weakly Supervised Multi-Task Learning For Concept-Based Explainability |
| US20220083915A1 | Discriminative Machine Learning System For Optimization Of Multiple Objectives |
| US20220027679A1 | Human-In-The-Loop Evaluation For Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
| US20220012542A1 | Bandit-Based Techniques For Fairness-Aware Hyperparameter Optimization |
| EP3414670B1 | Automatic Detection Of Points Of Compromise |
| EP3669317A4 | Computer Memory Management During Real-Time Fraudulent Transaction Analysis |
| EP3850531A1 | Semantic-Aware Feature Engineering |
| EP3887920A4 | Graph Decomposition For Fraudulent Transaction Analysis |
| EP3888023A4 | Automatic Model Monitoring For Data Streams |
| EP3888038A4 | Automated Rules Management System |
| EP4042255A1 | Weakly Supervised Multi-Task Learning For Concept-Based Explainability |
| EP3887931A4 | Graph Search And Visualization For Fraudulent Transaction Analysis |
| EP4038469A1 | Hierarchical Machine Learning Model For Performing & Decision Task And An Explanation Task |
| EP4035098A1 | A Model-Agnostic Approach To Interpreting Sequence Predictions |
| EP4026308A1 | Discriminative Machine Learning System For Optimization Of Multiple Objectives |
| EP4016430A1 | Graph Traversal For Measurement Of Fraudulent Nodes |
| EP4000034A1 | Distributed Streaming System Supporting Real-Time Sliding Windows |
| EP3997630A1 | Human-In-The-Loop Evaluation For Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
| EP3997626A1 | Active Learning Annotation System That Does Not Require Historical Data |
| EP3997592A1 | Interleaved Sequence Recurrent Neural Networks For Fraud Detection |
| EP3997547A1 | Bandit-Based Techniques For Fairness-Aware Hyperparameter Optimization |
| WO2017139035A1 | Automatic Detection Of Points Of Compromise |
| WO2019036420A1 | Computer Memory Management During Real-Time Fraudulent Transaction Analysis |
| WO2020231610A1 | Automatic Model Monitoring For Data Streams |
| WO2020053652A1 | Semantic-Aware Feature Engineering |
| WO2021242920A1 | Active Learning Annotation System That Does Not Require Historical Data |
| WO2021163333A1 | Interleaved Sequence Recurrent Neural Networks For Fraud Detection |
| WO2021096684A1 | Automated Rules Management System |
| WO2021086794A1 | Graph Search And Visualization For Fraudulent Transaction Analysis |
| WO2022150062A1 | Automated Feature Monitoring For Data Streams |
| WO2022081713A1 | A Model-Agnostic Approach To Interpreting Sequence Predictions |
| WO2022060709A1 | Discriminative Machine Learning System For Optimization Of Multiple Objectives |
| WO2022035511A1 | Distributed Streaming System Supporting Real-Time Sliding Windows |
| WO2022020597A1 | Human-In-The-Loop Evaluation For Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
| WO2022011150A1 | Bandit-Based Techniques For Fairness-Aware Hyperparameter Optimization |
| AU2019340890A1 | Semantic-Aware Feature Engineering |
| CA3112068A1 | Semantic-Aware Feature Engineering |
| DE602016046501T2 | Automatic Detection Of Compromise Points |
| SG11202102325PA | Semantic-Aware Feature Engineering |
| ES2844399T8 | Automatic Detection Of Commitment Points |
