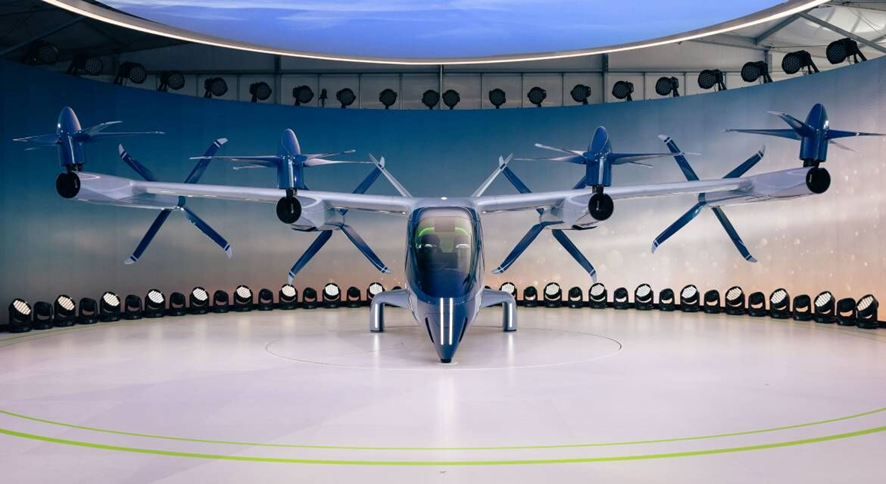
Hyundai recently unveiled its S-A2 eVTOL aircraft at CES 2024, showcasing a major leap in urban air mobility. This innovative air taxi, designed for four passengers and a pilot, features quiet, efficient rotors and robust safety systems. It aims to address urban travel needs with speeds up to 120 mph and ranges suitable for typical city trips. Hyundai plans to enter the market by 2028, focusing on affordability and sustainability. With advanced battery systems, noise reduction technology, and strict safety standards, Hyundai is set to lead the future of urban air transportation.

What are the functions of Hyundai Flying Car?
- Electric Propulsion System: Uses electric motors for quieter and more efficient flight with reduced emissions.
- Vertical Take-Off and Landing (VTOL): Capable of vertical take-offs and landings, eliminating the need for runways.
- Advanced Composite Materials: Built with lightweight, durable materials to enhance performance and efficiency.
- Autonomous Navigation Systems: Features cutting-edge autonomous technology for safe and precise navigation.
- Battery Technology: Employs advanced batteries for efficient power storage and quick recharging.
- Safety Features: Incorporates multiple redundancies and sensors for enhanced safety and reliability.

Which Key Patents are behind Hyundai’s eVTOL aircraft?
We’ve analyzed key patents related to Hyundai Air Taxi. Read the summary below and discover the ingenuity behind this breakthrough innovation revolutionizing future of urban air mobility!
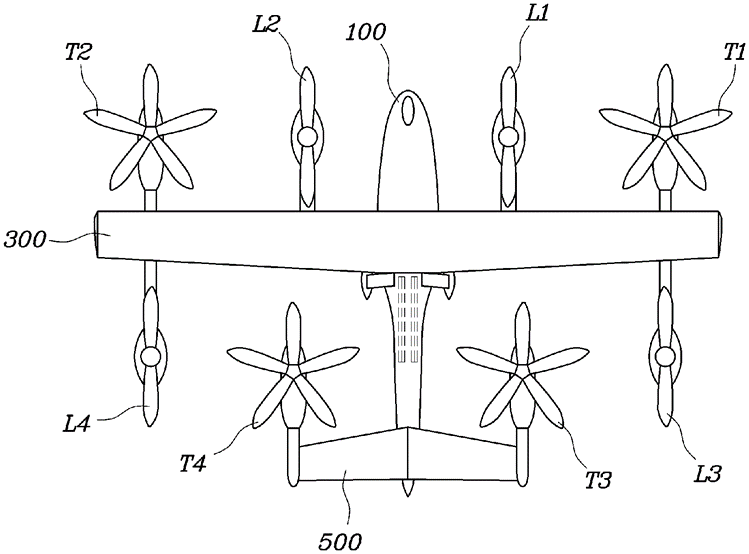
The patent, US11643200B2, discloses the components of Hyundai’s eVTOL aircraft:
- Fuselage: Contains boarding space and gate.
- Wings: Multiple wings attached to the fuselage.
- Rotors: Includes tilting rotors for lift and cruise, and lifting rotors for stability.
The figure below shows a lifting state of the takeoff and landing air mobility.
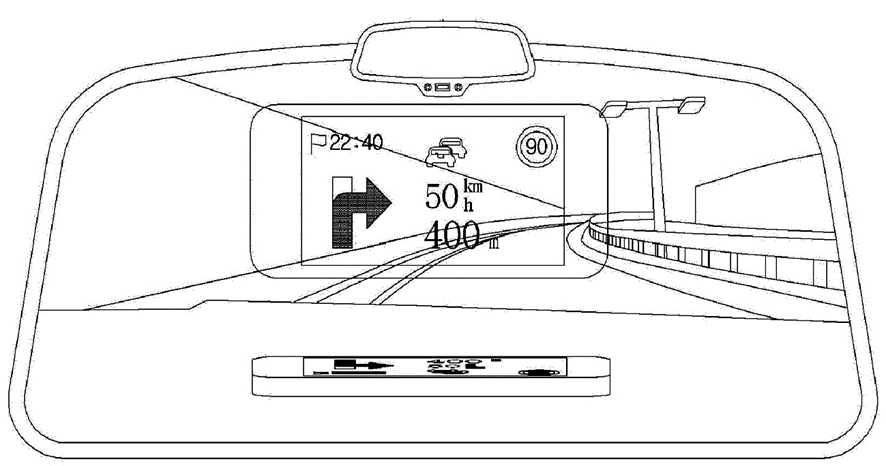
The patent, EP3858702A2, describes a method for providing driving guideline in Hyundai’s Flying Car, which includes these steps as illustrated in the following figure:
- Triggering: Initiating a driving guideline provision instruction in the moving object.
- Generating: Creating a driving guideline based on the triggered instruction.
- Outputting: Displaying the generated driving guideline.
- Driving: Operating the eVTOL based on the provided guideline.
The figure below illustrates an augmented reality navigation system in a moving object.
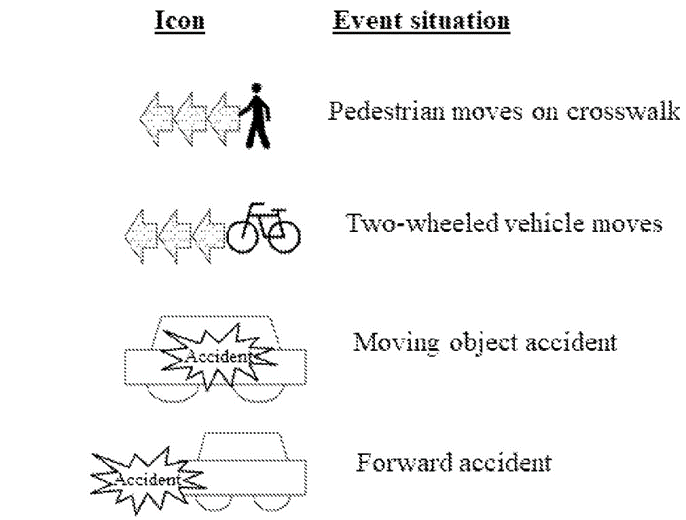
The patent, US11840221B2, describes Hyundai’s advanced collision detection technology for enhancing the safety and reliability of urban air travel:
- Detection: Identifies objects and events in the aircraft’s path.
- Situation Assessment: Categorizes situations as emergency, manageable or general based on detected objects and events.
- Warning Transmission: Determines if a warning message can be sent in manageable situations.
- Collision Alert: Sends collision possibility information using a warning alarm system if the warning message cannot be transmitted.
The figure below showcases the information that is output through a display region.
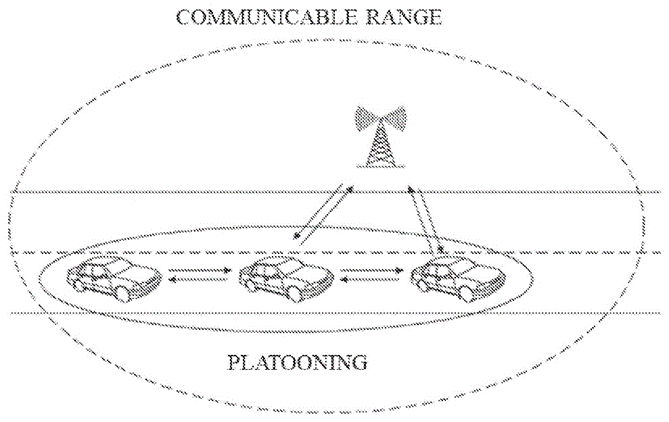
The patent, US20210240203A1, describes the method for autonomous vehicle platooning using intelligent transportation system (ITS) infrastructure.
- Autonomous Driving and Platooning: The system sets a moving path and determines if platooning is allowed.
- Intelligent Transportation System (ITS): Transmits moving path information to the ITS infrastructure when approaching its range.
- Platooning Coordination: Receives platooning information from the ITS, which groups compatible moving objects based on their paths.
- Platooning Execution: Performs platooning based on the received information.
The figure below illustrates a method of performing platooning of the moving object.
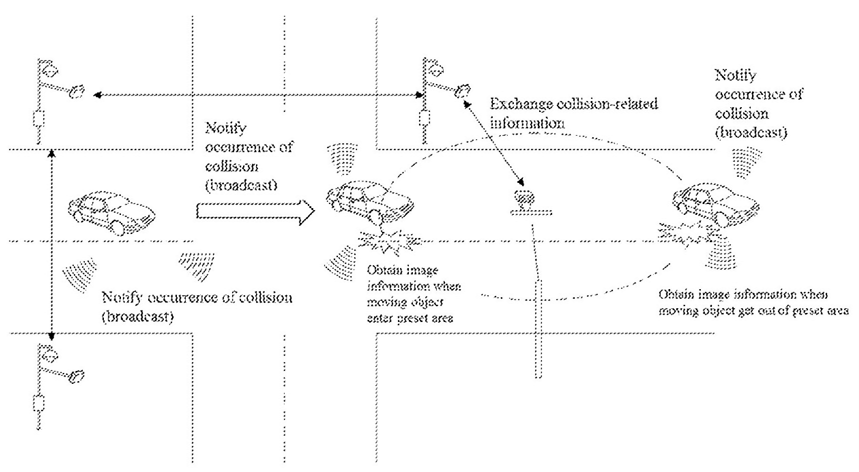
The patent, US20210237725A1, describes the eVTOL aircraft featuring a sophisticated moving object escape prevention method:
- Autonomous Control: Driven by a processor for autonomous navigation.
- Collision Detection: Processor detects and responds to collisions.
- Intelligent Notification: Sends collision alerts and position data to Intelligent Transportation System Infrastructure (ITSI).
- Escape Prevention: ITSI evaluates if the vehicle has moved, sending accident handling info if it hasn’t, or an escape warning if it has.
The figure below showcases a method of identifying an escaping vehicle when an accident occurs to an autonomous vehicle.
As Hyundai propels into the future with its flying car, it stands alongside competitors like Uber Elevate, Joby Aviation and Lilium, all working on similar urban air mobility solutions. However, Hyundai’s eVTOL distinguishes itself with its unique combination of advanced composite materials, autonomous navigation systems and an innovative escape prevention method. These features ensure a safer, quieter and more efficient flight experience. The transformative potential of Hyundai’s air taxi lies in its ability to revolutionize urban transportation, making air travel accessible, eco-friendly and seamlessly integrated into daily life.
Need to know anything else? We got you covered!