The Xpeng Flying Car isn’t just a futuristic dream; it represents a transformative leap in personal transportation. By combining advanced automotive engineering with cutting-edge aeronautics, Xpeng is leading the charge toward a future where the boundaries between road and air travel blur. Recently, Xpeng’s latest prototype successfully completed a series of rigorous flight tests, marking a critical step closer to making this groundbreaking technology available to the public.
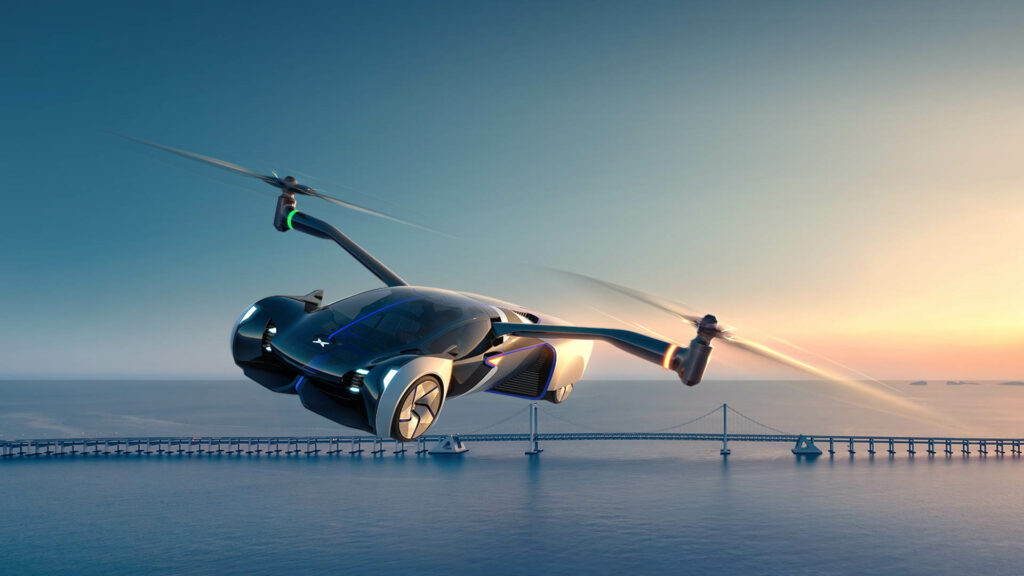

Image : Source
How does Xpeng Flying Car Work?
Adaptive Wing and Rotor Deployment: The Xpeng flying car features a highly specialized mechanism for wing and rotor deployment. When transitioning from driving to flying mode, the vehicle’s wings and rotors automatically extend from the body, utilizing a combination of hydraulic and electric actuators to achieve rapid and precise positioning.
Vertical Lift via Distributed Electric Propulsion: The vehicle utilizes a distributed electric propulsion system, with multiple rotors strategically placed to provide balanced vertical lift. This system ensures stability during takeoff and landing, distributing the thrust evenly across the vehicle’s structure and allowing for controlled vertical movement.
Integrated Flight Control System: The Xpeng flying car is equipped with an advanced flight control system that integrates real-time data from various sensors, including gyroscopes, accelerometers, and GPS. This system continuously adjusts the rotor speeds and wing angles to maintain optimal flight conditions, ensuring a smooth and stable flight experience.
Structural Rigidity with Lightweight Design: The chassis of the Xpeng flying car is engineered using high-strength, lightweight materials like carbon fiber composites. This design provides the necessary structural rigidity to withstand the stresses of both road and air travel while minimizing overall weight, which is critical for achieving efficient flight performance.
Performance of Xpeng AeroHT Flying Car
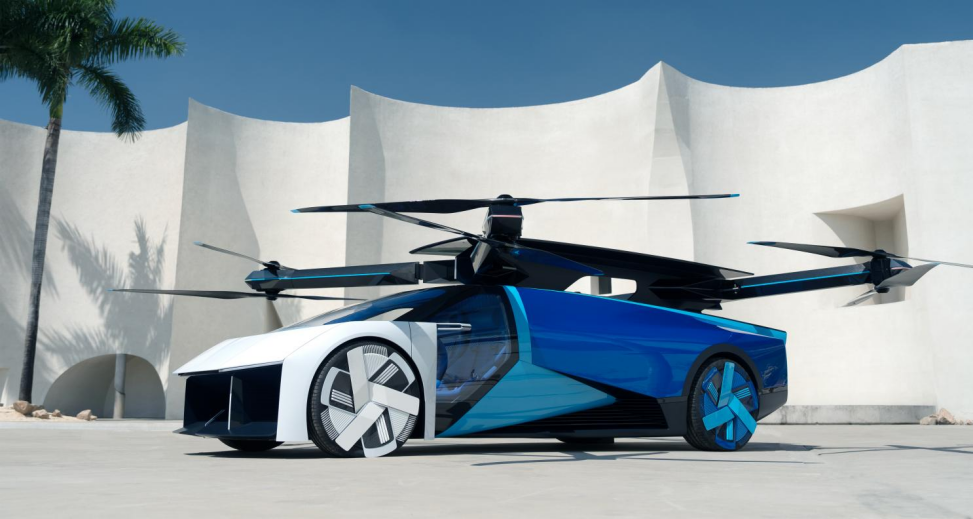

Image : Source
Ground Performance: On the road, the Xpeng flying car can reach speeds of up to 125 km/h (78 mph), powered by an electric drivetrain that delivers instant torque for rapid acceleration. The vehicle’s lightweight design, coupled with its aerodynamic profile, allows for agile handling and efficient energy use, making it suitable for both urban commuting and highway driving.
Airborne Performance: When in flight mode, the Xpeng flying car can achieve a cruising speed of approximately 160 km/h (100 mph). The vehicle’s VTOL (Vertical Takeoff and Landing) capability allows it to take off vertically and transition smoothly to forward flight. It has a flight range of around 35-40 km (22-25 miles) per charge, making it ideal for short to medium-distance travel across congested urban areas or between nearby cities.
Battery Performance: The Xpeng flying car is equipped with a high-capacity battery system, boasting a total energy capacity of around 80 kWh. This battery supports both driving and flying modes, providing a driving range of up to 500 km (310 miles) on a single charge in ground mode. In the air, the battery’s energy management system ensures optimal power distribution to the rotors, maximizing flight time while maintaining safety and stability.
Charging Time: The vehicle’s battery system supports fast charging, allowing it to recharge from 0% to 80% in approximately 45 minutes using a high-power DC fast charger. For full charging, it typically takes about 1.5 hours. Additionally, the battery system includes regenerative braking and descent energy recovery features, which help extend the vehicle’s operational range and improve overall efficiency.
Energy Efficiency: The vehicle is equipped with a state-of-the-art battery system that supports both driving and flying modes. The batteries are optimized for high energy density, providing a long driving range and sufficient power for sustained flight. The energy management system also includes regenerative features, allowing the vehicle to recover energy during descent and braking, which contributes to overall efficiency.
Flying Car Patents
We’ve analyzed key patents related to Flying Car. Read the summary below and discover the ingenious innovations behind this breakthrough technology!
The patent CN113835440A focuses on improving the stability and safety of flying cars during takeoff, landing, and in-flight transitions. It introduces a system that adjusts the vehicle’s center of gravity and power distribution, solving the problem of maintaining balance and control, thus enhancing the overall safety and reliability of flying cars.
This patent CN115949316A outlines a method to control vehicle door opening by analyzing external environment images, eliminating the need for costly radar sensors. It projects and analyzes obstacles to determine safe door operation, reducing manufacturing and maintenance costs while extending the lifespan of distance detection devices.
This patent CN112947563A describes a method for controlling an aircraft (like a drone) to return to a moving vehicle, such as a car. Instead of the aircraft only returning to a fixed point, the system uses the vehicle’s navigation data to determine a meeting point where the aircraft can return to the vehicle while it’s still in motion.
This allows the aircraft to safely land on the vehicle without requiring it to stop. The solution addresses the challenge of coordinating a moving vehicle with a returning aircraft, making the process more efficient and practical, especially for scenarios where stopping the vehicle isn’t feasible.
This patent CN110949550A introduces a system that automatically adjusts a vehicle’s tail wing based on real-time driving conditions, such as acceleration or deceleration. Unlike traditional systems that only respond to speed changes, this method adapts the tail wing’s position raising, lowering, or tilting to enhance stability and aerodynamics in various scenarios, improving both performance and user experience. It solves the problem of static tail wing control by providing a more dynamic and responsive solution.
Xpeng’s flying car stands out among competitors like AeroMobil, Terrafugia, and PAL-V by seamlessly blending advanced automotive and aviation technologies. Unlike others, Xpeng offers a practical, scalable solution for urban mobility with features like vertical takeoff, hybrid propulsion, and autonomous capabilities. This positions the Xpeng Flying Car to revolutionize travel, combining the ease of driving with the freedom of flight, and leading the way into a new era of transportation.
What other companies are filing patents in the flying car space? Request a patent landscape around this technology by filling out the form below:


