What if the future of clean mobility does not abandon internal combustion-but instead adds two more strokes to reinvent it?
As automakers search for alternatives beyond battery-electric vehicles, hydrogen combustion is re-emerging as a serious contender. Among the concepts gaining renewed attention is the six-stroke engine, an extended-cycle architecture designed to extract more energy, control heat, and improve emissions performance.
Within this evolving landscape, Mazda’s hydrogen six-stroke engine concept reflects a focused effort to adapt extended engine cycles for the unique combustion characteristics of hydrogen fuel. Rather than relying on the limitations of conventional four-stroke designs, Mazda’s approach explores how additional stroke phases can be used to stabilize combustion, manage in-cylinder temperatures, and improve overall efficiency.
This work aligns with Mazda’s broader multi-solution strategy toward carbon neutrality, one that balances electrification with continued innovation in internal combustion technologies. By applying six-stroke architecture specifically to hydrogen engines, Mazda is contributing to the refinement of low-carbon combustion pathways that can coexist with electric powertrains.
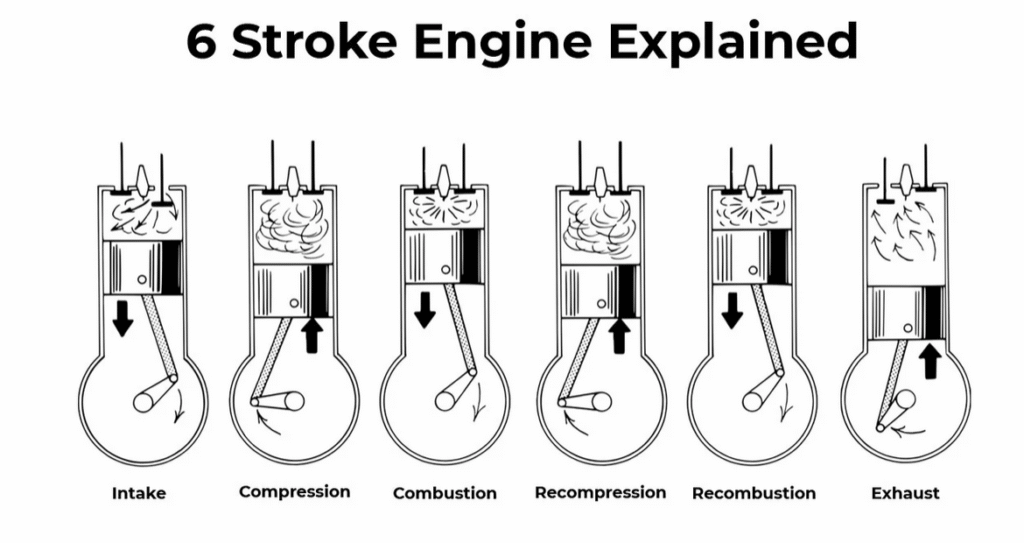
Current Challenges in Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engines
Hydrogen combustion presents distinct engineering challenges that limit large-scale adoption:
- High combustion temperatures, increasing NOx emissions
- Pre-ignition and backfire risks due to hydrogen’s low ignition energy
- Efficiency losses in four-stroke cycles not optimized for hydrogen
- Durability concerns caused by thermal and pressure fluctuations
The Mazda hydrogen six stroke engine patent addresses these issues by redesigning the engine cycle itself rather than relying solely on emissions aftertreatment or control software.
Check out mazda’s six stroke hydrogen engine patents filed in 2025:
Patent behind Mazda’s Six-Stroke Hydrogen Engine
| Publication No | Assignee | Problem Addressed | Solution Proposed | R&D / Industry Impact |
| EP4603692A1 | Mazda Motor Corporation | Inefficiency and heat buildup in hydrogen four-stroke engines | Six-stroke cycle with additional expansion and cooling phases | Improves hydrogen combustion efficiency and engine longevity |
| JP2024110816A | Mazda Motor Corporation | Abnormal combustion and pre-ignition | Hydrogen-optimized stroke sequencing and ignition timing | Enhances combustion stability and safety |
| JP2024110818A | Mazda Motor Corporation | NOx emissions and component stress | Integrated thermal control within six-stroke architecture | Supports emissions compliance and durability targets |
Get the list of six stroke engine patents. Discover the problems they solve and the solutions they offer. Fill out the form to access it now!
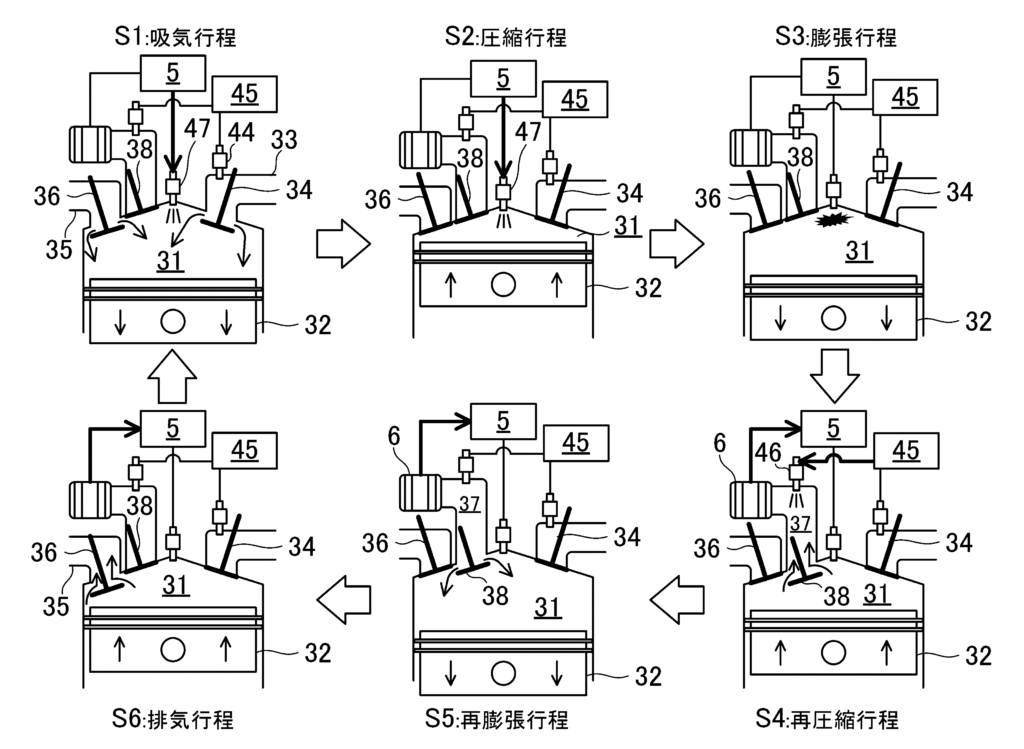
How the Mazda Hydrogen Six Stroke Engine Works
Based on the patent disclosures, the six-stroke hydrogen engine introduces:
- An extra expansion stroke to extract more energy from hydrogen combustion
- A dedicated cooling or scavenging stroke to lower in-cylinder temperature
- Improved pressure and heat management before the next combustion cycle
This configuration allows hydrogen’s fast flame speed and wide flammability range to be used more efficiently, rather than becoming a liability.
Regulation & Industry Standards for Six-Stroke Hydrogen Engines
| Regulatory Area | Current Status | Impact on Six-Stroke Hydrogen Engines |
| Emissions Regulations | Governed by existing ICE standards (e.g., Euro, U.S. EPA) | Must meet NOx limits despite zero CO₂ emissions; engine cycle design must support emissions compliance |
| Hydrogen Safety Standards | Well-established global standards | Fuel storage, leak detection, refueling, and crash safety requirements apply regardless of stroke count |
| Engine Certification | Certified under conventional ICE frameworks | Regulators evaluate emissions, durability, and safety outcomes rather than engine architecture |
| Six-Stroke–Specific Rules | No dedicated regulations yet | Creates uncertainty in testing methods, validation cycles, and approval timelines |
| Regional Policy Differences | Varies by market | Some regions support hydrogen combustion, while others prioritize EV-only strategies |
| Industry Standards Development | Still evolving | OEMs and industry groups are engaging regulators to ensure fair evaluation of advanced combustion concepts |
Use Cases for the Mazda Hydrogen Six Stroke Engine
Potential applications include:
- Hydrogen-powered passenger vehicles
- Hybrid hydrogen-electric powertrains
- Commercial and fleet vehicles requiring fast refueling
- Multi-fuel platforms compatible with synthetic fuels
Because the architecture builds on internal combustion fundamentals, it may offer lower cost and faster scalability than fuel-cell alternatives.
Future Aspects of Six-Stroke Hydrogen Engines
The future of six-stroke hydrogen engines will be shaped by a combination of regulatory clarity, technology maturity, and infrastructure development. As emissions regulations evolve, hydrogen internal combustion engines are increasingly likely to be recognized as a low-carbon solution alongside electrification.
Improvements in combustion control and thermal management are expected to reduce NOx emissions and improve efficiency, making six-stroke designs more compliant with future standards. Integration with hybrid systems could further enhance performance and fuel efficiency while lowering overall emissions.
Over time, design simplification and scale may help reduce costs, improving commercial viability. Fuel flexibility, including compatibility with synthetic fuels, adds strategic resilience. Ultimately, six-stroke hydrogen engines are positioned as a complementary, transition-ready technology rather than a replacement for electric vehicles.
Conclusion
The Mazda hydrogen six stroke engine patent demonstrates how rethinking engine fundamentals can unlock new performance and emissions benefits for hydrogen combustion. By extending the engine cycle and embedding thermal control into the combustion process, Mazda is positioning hydrogen ICE technology as a credible complement to electrification.
For automotive strategists, suppliers, and IP analysts, these patents signal that advanced combustion innovation remains highly relevant in the transition to carbon-neutral mobility.
Interested in a deeper hydrogen six stroke engine patent analysis?
Request a tailored report or claim-to-product mapping to explore competitor strategies.

